Helicobacter pylori induction of the gastrin promoter through GC-rich DNA elements
- PMID: 21083750
- PMCID: PMC3306726
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2010.00787.x
Helicobacter pylori induction of the gastrin promoter through GC-rich DNA elements
Abstract
Background: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection has been linked to the development of chronic gastritis, duodenal ulcer disease, and gastric cancer. Helicobacter pylori- infected patients and animal models develop hypergastrinemia, chronic gastritis, and gastric atrophy. Since gastrin is an important regulator of gastric acid secretion and cell growth, H. pylori regulation of this hormone has been implicated in its pathogenesis.
Objectives: To investigate the effect of H. pylori on gastrin gene expression in mice and of human bacterial isolates on gastrin mRNA expressed in a human cell line.
Methods: Gastrin mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR in H. pylori-infected mice. H. pylori were co-cultured with AGS cells to study regulation of human gastrin gene expression. Various MAP kinases were implicated in signal transduction from the bacteria using specific inhibitors. Gastrin reporter constructs and gel shift assays were used to map DNA responsive elements.
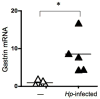
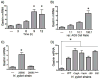
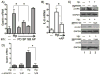
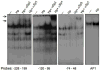
Results: In addition to an increase in gastrin mRNA in H. pylori-infected mice, H. pylori induced the endogenous human gastrin gene through MAP kinase-dependent signaling but not NFκB-dependent signaling. Activation of gastrin through MAPK signaling did not require CagA or VacA virulence factors. Transfection studies demonstrated that a GC-rich motif mediated H. pylori-induction of the gastrin promoter and that the motif inducibly binds Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors.
Conclusions: Direct contact of live H. pylori bacteria with human cells is sufficient to induce gastrin gene expression.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori-Induced HB-EGF Upregulates Gastrin Expression via the EGF Receptor, C-Raf, Mek1, and Erk2 in the MAPK Pathway.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jan 15;7:541. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00541. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29379775 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori potentiates epithelial:mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer: links to soluble HB-EGF, gastrin and matrix metalloproteinase-7.Gut. 2010 Aug;59(8):1037-45. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.199794. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Gut. 2010. PMID: 20584780 Free PMC article.
-
Human gastrin mRNA expression up-regulated by Helicobacter pylori CagA through MEK/ERK and JAK2-signaling pathways in gastric cancer cells.Gastric Cancer. 2011 Oct;14(4):322-31. doi: 10.1007/s10120-011-0044-2. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Gastric Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21509655
-
Mouse model of Helicobacter pylori infection: studies of gastric function and ulcer healing.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999 Mar;13(3):333-46. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1999.00476.x. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1999. PMID: 10102967
-
Gastric cancer and gastrin: on the interaction of Helicobacter pylori gastritis and acid inhibitory induced hypergastrinemia.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep;54(9):1118-1123. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2019.1663446. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31524029 Review.
Cited by
-
Helicobacter pylori-Induced HB-EGF Upregulates Gastrin Expression via the EGF Receptor, C-Raf, Mek1, and Erk2 in the MAPK Pathway.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jan 15;7:541. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00541. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29379775 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity in bacterium-host interactions within the species Helicobacter heilmannii sensu stricto.Vet Res. 2013 Jul 29;44(1):65. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-44-65. Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 23895283 Free PMC article.
-
How Helicobacter pylori infection controls gastric acid secretion.J Gastroenterol. 2012 Jun;47(6):609-18. doi: 10.1007/s00535-012-0592-1. Epub 2012 May 8. J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22565637 Review.
-
Dysregulation of MiR-30a-3p/Gastrin Enhances Tumor Growth and Invasion throughSTAT3/MMP11 Pathway in Gastric Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Aug 25;13:8475-8493. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S235022. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32922036 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrin: From Physiology to Gastrointestinal Malignancies.Function (Oxf). 2021 Nov 26;3(1):zqab062. doi: 10.1093/function/zqab062. eCollection 2022. Function (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 35330921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Peterson WL. Helicobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1043–1048. - PubMed
-
- Parsonnet J, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1267–1271. - PubMed
-
- Peek RM, Jr, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Covacci A, Telford JL, Del Giudice G, Parsonnet J, Rappuoli R. Helicobacter pylori virulence and genetic geography. Science. 1999;284:1328–1333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

