Thoracoscopic-assisted repair of a bochdalek hernia in an adult: a case report
- PMID: 21083878
- PMCID: PMC3000846
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-366
Thoracoscopic-assisted repair of a bochdalek hernia in an adult: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Bochdalek hernia is a congenital defect of the diaphragm that usually presents in the neonatal period with life-threatening cardiorespiratory distress. It is rare for Bochdalek hernias to remain silent until adulthood. Once a Bochdalek hernia has been diagnosed, surgical treatment is necessary to avoid complications such as perforation and necrosis.
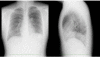
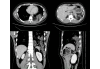
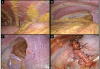
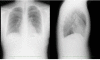
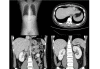
Case presentation: We present a 17-year-old Japanese boy with left-upper-quadrant pain for two months. Chest radiography showed an elevated left hemidiaphragm. Computed tomography revealed a congenital diaphragmatic hernia. The spleen and left colon had been displaced into the left thoracic cavity through a left posterior diaphragmatic defect. We diagnosed a Bochdalek hernia. Surgical treatment was performed via a thoracoscopic approach. The boy was placed in the reverse Trendelenburg position and intrathoracic pressure was increased by CO2 gas insufflations. This is a very useful procedure for reducing herniated contents and we were able to place the herniated organs safely back in the peritoneal cavity. The diaphragmatic defect was too large to close with thoracoscopic surgery alone. Small incision thoracotomy was required and primary closure was performed. His postoperative course was uneventful and there has been no recurrence of the diaphragmatic hernia to date.
Conclusion: Thoracoscopic surgery, performed with the boy in the reverse Trendelenburg position and using CO2 gas insufflations in the thoracic cavity, was shown to be useful for Bochdalek hernia repair.
Figures
References
-
- Cosenza UM, Raschella GF, Giacomelli L, Scicchitano F, Simone M, Cancrini G, Zofrea P, Cancrini A. The Bochdalek hernia in the adult: case report and review of the literature. G Chir. 2004;25:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Mullins ME, Stein J, Saini SS, Mueller PR. Prevalence of incidental Bochdalek's hernia in a large adult population. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Willemse P, Schutte PR, Plaisier PW. Thoracoscopic repair of a Bochdalek hernia in an adult. Surg Endosc. 2003;17:162. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

