Reconstruction and analysis of genome-scale metabolic model of a photosynthetic bacterium
- PMID: 21083885
- PMCID: PMC3009638
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-156
Reconstruction and analysis of genome-scale metabolic model of a photosynthetic bacterium
Abstract
Background: Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 is a cyanobacterium considered as a candidate photo-biological production platform--an attractive cell factory capable of using CO2 and light as carbon and energy source, respectively. In order to enable efficient use of metabolic potential of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803, it is of importance to develop tools for uncovering stoichiometric and regulatory principles in the Synechocystis metabolic network.
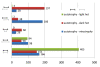
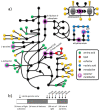
Results: We report the most comprehensive metabolic model of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 available, iSyn669, which includes 882 reactions, associated with 669 genes, and 790 metabolites. The model includes a detailed biomass equation which encompasses elementary building blocks that are needed for cell growth, as well as a detailed stoichiometric representation of photosynthesis. We demonstrate applicability of iSyn669 for stoichiometric analysis by simulating three physiologically relevant growth conditions of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803, and through in silico metabolic engineering simulations that allowed identification of a set of gene knock-out candidates towards enhanced succinate production. Gene essentiality and hydrogen production potential have also been assessed. Furthermore, iSyn669 was used as a transcriptomic data integration scaffold and thereby we found metabolic hot-spots around which gene regulation is dominant during light-shifting growth regimes.
Conclusions: iSyn669 provides a platform for facilitating the development of cyanobacteria as microbial cell factories.
Figures


References
-
- Schopf J. In: The ecology of cyanobacteria. Whitton B, Potts M, editor. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2000. The Fossil Record: Tracing the Roots of the Cyanobacterial Lineage; pp. 13–35.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

