Procalcitonin reflects bacteremia and bacterial load in urosepsis syndrome: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 21083886
- PMCID: PMC3220019
- DOI: 10.1186/cc9328
Procalcitonin reflects bacteremia and bacterial load in urosepsis syndrome: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Guidelines recommend that two blood cultures be performed in patients with febrile urinary tract infection (UTI), to detect bacteremia and help diagnose urosepsis. The usefulness and cost-effectiveness of this practice have been criticized. This study aimed to evaluate clinical characteristics and the biomarker procalcitonin (PCT) as an aid in predicting bacteremia.
Methods: A prospective observational multicenter cohort study included consecutive adults with febrile UTI in 35 primary care units and 8 emergency departments of 7 regional hospitals. Clinical and microbiological data were collected and PCT and time to positivity (TTP) of blood culture were measured.
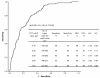
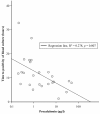
Results: Of 581 evaluable patients, 136 (23%) had bacteremia. The median age was 66 years (interquartile range 46 to 78 years) and 219 (38%) were male. We evaluated three different models: a clinical model including seven bed-side characteristics, the clinical model plus PCT, and a PCT only model. The diagnostic abilities of these models as reflected by area under the curve of the receiver operating characteristic were 0.71 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.66 to 0.76), 0.79 (95% CI: 0.75 to 0.83) and 0.73 (95% CI: 0.68 to 0.77) respectively. Calculating corresponding sensitivity and specificity for the presence of bacteremia after each step of adding a significant predictor in the model yielded that the PCT > 0.25 μg/l only model had the best diagnostic performance (sensitivity 0.95; 95% CI: 0.89 to 0.98, specificity 0.50; 95% CI: 0.46 to 0.55). Using PCT as a single decision tool, this would result in 40% fewer blood cultures being taken, while still identifying 94 to 99% of patients with bacteremia.The TTP of E. coli positive blood cultures was linearly correlated with the PCT log value; the higher the PCT the shorter the TTP (R(2) = 0.278, P = 0.007).
Conclusions: PCT accurately predicts the presence of bacteremia and bacterial load in patients with febrile UTI. This may be a helpful biomarker to limit use of blood culture resources.
Figures
Comment in
-
In critically ill patients the procalcitonin level can be misleading.Crit Care. 2011;15(2):422. doi: 10.1186/cc10132. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21542896 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

