Association of serum markers with improvement in clinical response measures after treatment with golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite receiving methotrexate: results from the GO-FORWARD study
- PMID: 21083889
- PMCID: PMC3046519
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3188
Association of serum markers with improvement in clinical response measures after treatment with golimumab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite receiving methotrexate: results from the GO-FORWARD study
Abstract
Introduction: The goal of this study was to identify serum markers that are modulated by treatment with golimumab with or without methotrexate (MTX) and are associated with clinical response.
Methods: Sera were collected at weeks 0 and 4 from a total of 336 patients (training dataset, n = 100; test dataset, n = 236) from the GO-FORWARD study of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite MTX. Patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo plus MTX; golimumab, 100 mg plus placebo; golimumab, 50 mg plus MTX; or golimumab, 100 mg plus MTX. Subcutaneous injections were administered every 4 weeks. Samples were tested for select inflammatory, bone, and cartilage markers and for protein profiling using multianalyte profiles.
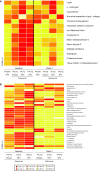
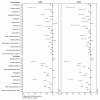
Results: Treatment with golimumab with or without MTX resulted in significant decreases in a variety of serum proteins at week 4 as compared with placebo plus MTX. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 20, ACR 50, and Disease Activity Score (DAS) 28 responders showed a distinct biomarker profile compared with nonresponding patients.
Conclusions: ACR 20 and ACR 50 responders among the golimumab/golimumab + MTX-treated patients had a distinct change from baseline to week 4 in serum protein profile as compared with nonresponders. Some of these changed markers were also associated with multiple clinical response measures and improvement in outcome measures in golimumab/golimumab + MTX-treated patients. Although the positive and negative predictive values of the panel of markers were modest, they were stronger than C-reactive protein alone in predicting clinical response to golimumab.
Trial registration: http://ClinicalTrials.gov identification number: NCT00264550.
Figures
References
-
- Listing J, Rau R, Muller B, Alten R, Gromnica-Ihle E, Hagemann D, Zink A. HLA-DRB1 genes, rheumatoid factor, and elevated C-reactive protein: independent risk factors of radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis. Berlin Collaborating Rheumatological Study Group. J Rheumatol. 2000;27:2100–2109. - PubMed
-
- Geusens PP, Landewe RB, Garnero P, Chen D, Dunstan CR, Lems WF, Stinissen P, van der Heijde DM, van der Linden S, Boers M. The ratio of circulating osteoprotegerin to RANKL in early rheumatoid arthritis predicts later joint destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1772–1777. doi: 10.1002/art.21896. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Emery P, Bathon JM, Keystone E, Maini RN, Kalden JR, Schiff M, Baker D, Han C, Han J, Bala M. Predictors of joint damage in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis treated with high-dose methotrexate with or without concomitant infliximab: results from the ASPIRE trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:702–710. doi: 10.1002/art.21678. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

