Efficacy of engineered FVIII-producing skeletal muscle enhanced by growth factor-releasing co-axial electrospun fibers
- PMID: 21084118
- PMCID: PMC3053058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.049
Efficacy of engineered FVIII-producing skeletal muscle enhanced by growth factor-releasing co-axial electrospun fibers
Abstract
Co-axial electrospun fibers can offer both topographical and biochemical cues for tissue engineering applications. In this study, we demonstrate the sustained treatment of hemophilia through a non-viral, tissue engineering approach facilitated by growth factor-releasing co-axial electrospun fibers. FVIII-producing skeletal myotubes were first engineered on aligned electrospun fibers in vitro, followed by implantation in hemophilic mice with or without a layer of core-shell electrospun fibers designed to provide sustained delivery of angiogenic or lymphangiogenic growth factors, which serves to stimulate the lymphatic or vascular systems to enhance the FVIII transport from the implant site into systemic circulation. Upon subcutaneous implantation into hemophilic mice, the construct seamlessly integrated with the host tissue within one month, and specifically induced either vascular or lymphatic network infiltration in accordance with the growth factors released from the electrospun fibers. Engineered constructs that induced angiogenesis resulted in sustained elevation of plasma FVIII and significantly reduced blood coagulation time for at least 2-months. Biomaterials-assisted functional tissue engineering was shown in this study to offer protein replacement therapy for a genetic disorder such as hemophilia.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
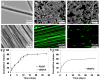
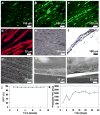

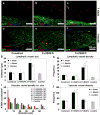

Similar articles
-
FVIII gene delivery by muscle electroporation corrects murine hemophilia A.J Gene Med. 2005 Apr;7(4):494-505. doi: 10.1002/jgm.683. J Gene Med. 2005. PMID: 15521095
-
Ex vivo gene therapy for hemophilia A that enhances safe delivery and sustained in vivo factor VIII expression from lentivirally engineered endothelial progenitors.Stem Cells. 2007 Oct;25(10):2660-9. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2006-0699. Epub 2007 Jul 5. Stem Cells. 2007. PMID: 17615271
-
Delivery of factor VIII gene into skeletal muscle cells using lentiviral vector.Yonsei Med J. 2010 Jan;51(1):52-7. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.1.52. Epub 2009 Dec 29. Yonsei Med J. 2010. PMID: 20046514 Free PMC article.
-
Development of improved factor VIII molecules and new gene transfer approaches for hemophilia A.Curr Gene Ther. 2003 Feb;3(1):27-41. doi: 10.2174/1566523033347417. Curr Gene Ther. 2003. PMID: 12553533 Review.
-
The evolving understanding of factor VIII binding sites and implications for the treatment of hemophilia A.Blood Rev. 2019 Jan;33:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 24. Blood Rev. 2019. PMID: 29866493 Review.
Cited by
-
Core-Shell Nanofibers of Polyvinylidene Fluoride-based Nanocomposites as Piezoelectric Nanogenerators.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Oct 13;12(10):2344. doi: 10.3390/polym12102344. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066181 Free PMC article.
-
Can microfluidics address biomanufacturing challenges in drug/gene/cell therapies?Regen Biomater. 2016 Jun;3(2):87-98. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbw009. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Regen Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27047674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation of multilayered polymeric structures using a novel four-needle coaxial electrohydrodynamic device.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014 Mar;35(6):618-23. doi: 10.1002/marc.201300777. Epub 2014 Feb 8. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2014. PMID: 24510905 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Applications of Coaxial and Emulsion Electrospinning Methods in the Field of Tissue Engineering.Biores Open Access. 2016 Aug 1;5(1):212-27. doi: 10.1089/biores.2016.0022. eCollection 2016. Biores Open Access. 2016. PMID: 27610268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology development in surgical applications: recent trends and developments.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Nov 24;28(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01429-4. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38001554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuang S, Rudnicki MA. The emerging biology of satellite cells and their therapeutic potential. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14(2):82–91. - PubMed
-
- Cao B, Deasy BM, Pollett J, Huard J. Cell therapy for muscle regeneration and repair. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2005;16(4):889–907. - PubMed
-
- Regulier E, Schneider BL, Deglon N, Beuzard Y, Aebischer P. Continuous delivery of human and mouse erythropoietin in mice by genetically engineered polymer encapsulated myoblasts. Gene Ther. 1998;5(8):1014–22. - PubMed
-
- MacColl GS, Goldspink G, Bouloux PMG. Using skeletal muscle as an artificial endocrine tissue. J Endocrinol. 1999;162(1):1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

