The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 induces cancer cell senescence
- PMID: 21084274
- PMCID: PMC3459262
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1977
The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 induces cancer cell senescence
Abstract
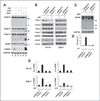
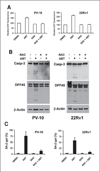
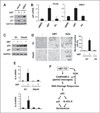
ABT-737, a small molecule cell-permeable Bcl-2 antagonist that acts by mimicking BH3 proteins, induces apoptotic cell death in multiple cancer types. However, when incubated with this agent many solid tumor cell lines do not undergo apoptosis. The current study reveals a novel mechanism whereby ABT-737 when added to apoptosis-resistant cancer cells has profound biologic effects. In PV-10 cells, a renal cell carcinoma that does not die after ABT-737 treatment, this agent induces a two-fold change in the transcription of nearly 430 genes. Many of these induced mRNA changes are in secreted proteins, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-11 and chemokines CXCL2 and CXCL5, or genes associated with an "inflammatory" phenotype. Strikingly, these gene changes are highly similar to those changes previously identified in cellular senescence. Brief exposure of apoptosis-resistant renal, lung and prostate cancer cell lines to ABT-737, although not capable of inducing cell death, causes the induction of senescence-associated β-galactosidase and inhibition of cell growth consistent with the induction of cellular senescence. Evidence indicates that the induction of senescence occurs as a result of reactive oxygen species elevation followed by low-level activation of the caspase cascade, insufficient to induce apoptosis, but sufficient to lead to minor DNA damage and increases in p53, p21, IL-6 and 8 proteins. By overexpression of a dominant-negative p53 protein, we show that ABT-737-induced cellular senescence is p53-dependent. Thus, in multiple cancer types in which ABT-737 is incapable of causing cell death, ABT-737 may have additional cellular activities that make its use as an anticancer agent highly attractive.
© 2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interests were disclosed.
Figures
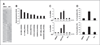



References
-
- Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA, et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature. 2005;435:677–681. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan D, Velankar M, Brahmandam M, Hideshima T, Podar K, Richardson P, et al. A novel Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L)/Bcl-w inhibitor ABT-737 as therapy in multiple myeloma. Oncogene. 2007;26:2374–2380. - PubMed
-
- Tagscherer KE, Fassl A, Campos B, Farhadi M, Kraemer A, Böck BC, et al. Apoptosis-based treatment of glioblastomas with ABT-737, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene. 2008;27:6646–6656. - PubMed
-
- Tahir SK, Yang X, Anderson MG, Morgan-Lappe SE, Sarthy AV, Chen J, et al. Influence of Bcl-2 family members on the cellular response of small-cell lung cancer cell lines to ABT-737. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1176–1183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

