Analysis of the polymerization initiation and activity of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2, an enzyme with glycosyltransferase and UDP-sugar hydrolase activity
- PMID: 21084307
- PMCID: PMC3023472
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136754
Analysis of the polymerization initiation and activity of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2, an enzyme with glycosyltransferase and UDP-sugar hydrolase activity
Abstract
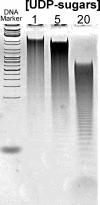
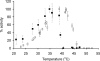
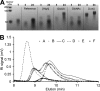
Heparosan synthase catalyzes the polymerization of heparosan (-4GlcUAβ1-4GlcNAcα1-)(n) by transferring alternatively the monosaccharide units from UDP-GlcUA and UDP-GlcNAc to an acceptor molecule. Details on the heparosan chain initiation by Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2 and its influence on the polymerization process have not been reported yet. By site-directed mutagenesis of PmHS2, the single action transferases PmHS2-GlcUA(+) and PmHS2-GlcNAc(+) were obtained. When incubated together in the standard polymerization conditions, the PmHS2-GlcUA(+)/PmHS2-GlcNAc(+) showed comparable polymerization properties as determined for PmHS2. We investigated the first step occurring in heparosan chain initiation by the use of the single action transferases and by studying the PmHS2 polymerization process in the presence of heparosan templates and various UDP-sugar concentrations. We observed that PmHS2 favored the initiation of the heparosan chains when incubated in the presence of an excess of UDP-GlcNAc. It resulted in a higher number of heparosan chains with a lower average molecular weight or in the synthesis of two distinct groups of heparosan chain length, in the absence or in the presence of heparosan templates, respectively. These data suggest that PmHS2 transfers GlcUA from UDP-GlcUA moiety to a UDP-GlcNAc acceptor molecule to initiate the heparosan polymerization; as a consequence, not only the UDP-sugar concentration but also the amount of each UDP-sugar is influencing the PmHS2 polymerization process. In addition, it was shown that PmHS2 hydrolyzes the UDP-sugars, UDP-GlcUA being more degraded than UDP-GlcNAc. However, PmHS2 incubated in the presence of both UDP-sugars favors the synthesis of heparosan polymers over the hydrolysis of UDP-sugars.
Figures


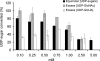
Similar articles
-
In vitro synthesis of heparosan using recombinant Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthase PmHS2.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Feb;85(6):1881-91. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2214-2. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 19756580 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of heparosan oligosaccharides by Pasteurella multocida PmHS2 single-action transferases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Sep;95(5):1199-210. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3813-2. Epub 2011 Dec 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22198719 Free PMC article.
-
Structure/function analysis of Pasteurella multocida heparosan synthases: toward defining enzyme specificity and engineering novel catalysts.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):7203-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.311704. Epub 2012 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22235128 Free PMC article.
-
Production methods for heparosan, a precursor of heparin and heparan sulfate.Carbohydr Polym. 2013 Mar 1;93(1):38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.046. Epub 2012 May 14. Carbohydr Polym. 2013. PMID: 23465899 Review.
-
Insights into the UDP-sugar selectivities of human UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGT): a molecular modeling perspective.Drug Metab Rev. 2015 Aug;47(3):335-45. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2015.1071835. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Drug Metab Rev. 2015. PMID: 26289097 Review.
Cited by
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae chitin biosynthesis activation by N-acetylchitooses depends on size and structure of chito-oligosaccharides.BMC Res Notes. 2011 Oct 27;4:454. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-454. BMC Res Notes. 2011. PMID: 22032207 Free PMC article.
-
Domain interactions control complex formation and polymerase specificity in the biosynthesis of the Escherichia coli O9a antigen.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 9;290(2):1075-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.622480. Epub 2014 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25422321 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Arabidopsis galacturonosyltransferases synthesize polymeric homogalacturonan by oligosaccharide acceptor-dependent or de novo synthesis.Plant J. 2022 Mar;109(6):1441-1456. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15640. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 34908202 Free PMC article.
-
Engineer P. multocida Heparosan Synthase 2 (PmHS2) for Size-Controlled Synthesis of Longer Heparosan Oligosaccharides.ACS Catal. 2020 Jun 5;10(11):6113-6118. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.0c01231. Epub 2020 May 11. ACS Catal. 2020. PMID: 33520345 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing glycoenzyme engineering for synthesis of bioactive oligosaccharides.Interface Focus. 2019 Apr 6;9(2):20180069. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2018.0069. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Interface Focus. 2019. PMID: 30842872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

