Basement membrane deposition of nidogen 1 but not nidogen 2 requires the nidogen binding module of the laminin gamma1 chain
- PMID: 21084308
- PMCID: PMC3023487
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149864
Basement membrane deposition of nidogen 1 but not nidogen 2 requires the nidogen binding module of the laminin gamma1 chain
Abstract
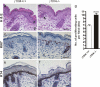
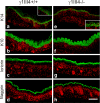
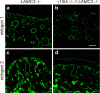
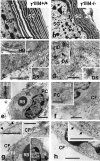
The nidogen-laminin interaction is proposed to play a key role in basement membrane (BM) assembly. However, though there are similarities, the phenotypes in mice lacking nidogen 1 and 2 (nidogen double null) differ to those of mice lacking the nidogen binding module (γ1III4) of the laminin γ1 chain. This indicates different cell- and tissue-specific functions for nidogens and their interaction with laminin and poses the question of whether the phenotypes in nidogen double null mice are caused by the loss of the laminin-nidogen interaction or rather by other unknown nidogen functions. To investigate this, we analyzed BMs, in particular those in the skin of mice lacking the nidogen binding module. In contrast to nidogen double null mice, all skin BMs in γ1III4-deficient mice appeared normal. Furthermore, although nidogen 1 deposition was strongly reduced, nidogen 2 appeared unchanged. Mice with additional deletion of the laminin γ3 chain, which contains a γ1-like nidogen binding module, showed a further reduction of nidogen 1 in the dermoepidermal BM; however, this again did not affect nidogen 2. This demonstrates that in vivo only nidogen 1 deposition is critically dependent on the nidogen binding modules of the laminin γ1 and γ3 chains, whereas nidogen 2 is independently recruited either by binding to an alternative site on laminin or to other BM proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Binding of mouse nidogen-2 to basement membrane components and cells and its expression in embryonic and adult tissues suggest complementary functions of the two nidogens.Exp Cell Res. 2002 Oct 1;279(2):188-201. doi: 10.1006/excr.2002.5611. Exp Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 12243745
-
Laminin gamma3 chain binds to nidogen and is located in murine basement membranes.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 10;280(23):22146-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501875200. Epub 2005 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15824114
-
Inhibition of basement membrane formation by a nidogen-binding laminin gamma1-chain fragment in human skin-organotypic cocultures.J Cell Sci. 2004 May 15;117(Pt 12):2611-22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01127. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15159456
-
Structural and genetic analysis of laminin-nidogen interaction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Oct 23;857:130-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10113.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9917838 Review.
-
Role of laminin-nidogen complexes in basement membrane formation during embryonic development.Experientia. 1995 Sep 29;51(9-10):901-13. doi: 10.1007/BF01921740. Experientia. 1995. PMID: 7556571 Review.
Cited by
-
Laminin-411 is a vascular ligand for MCAM and facilitates TH17 cell entry into the CNS.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040443. Epub 2012 Jul 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22792325 Free PMC article.
-
Laminin: loss-of-function studies.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Mar;74(6):1095-1115. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2381-0. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27696112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomics of post-stroke angiogenesis in the aged brain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2014 Mar 18;6:44. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00044. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24672479 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of the basement membrane component nidogen 2, but not of nidogen 1, results in increased lung metastasis in mice.J Histochem Cytochem. 2012 Apr;60(4):280-9. doi: 10.1369/0022155412436586. Epub 2012 Jan 19. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012. PMID: 22260998 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of non‑parenchymal hepatocytes in the process of hepatic fibrosis (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):364. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12003. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borradori L., Sonnenberg A. (1999) J. Invest. Dermatol. 112, 411–418 - PubMed
-
- McMillan J. R., Akiyama M., Shimizu H. (2003) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51, 1299–1306 - PubMed
-
- Timpl R., Brown J. C. (1996) Bioessays 18, 123–132 - PubMed
-
- Carlin B., Jaffe R., Bender B., Chung A. E. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 5209–5214 - PubMed
-
- Kimura N., Toyoshima T., Kojima T., Shimane M. (1998) Exp. Cell Res. 241, 36–45 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

