EAAC1 gene deletion alters zinc homeostasis and exacerbates neuronal injury after transient cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 21084597
- PMCID: PMC6633677
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2084-10.2010
EAAC1 gene deletion alters zinc homeostasis and exacerbates neuronal injury after transient cerebral ischemia
Abstract
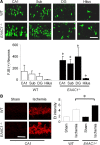
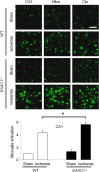
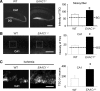
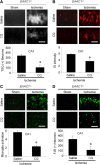
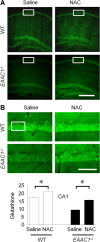
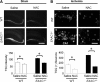
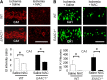
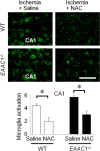
EAAC1 is a neuronal glutamate and cysteine transporter. EAAC1 uptake of cysteine provides substrate for neuronal glutathione synthesis, which plays a key role in both antioxidant defenses and intracellular zinc binding. Here we evaluated the role of EAAC1 in neuronal resistance to ischemia. EAAC1(-/-) mice subjected to transient cerebral ischemia exhibited twice as much hippocampal neuronal death as wild-type mice and a corresponding increase in microglial activation. EAAC1(-/-) mice also had elevated vesicular and cytosolic zinc concentrations in hippocampal CA1 neurons and an increased zinc translocation to postsynaptic neurons after ischemia. Treatment of the EAAC1(-/-) mice with N-acetyl cysteine restored neuronal glutathione concentrations and normalized basal zinc levels in the EAAC1(-/-) mice. Treatment of the EAAC1(-/-) mice with either N-acetyl cysteine or with zinc chelators reduced ischemia-induced zinc translocation, superoxide production, and neuron death. These findings suggest that cysteine uptake by EAAC1 is important for zinc homeostasis and neuronal antioxidant function under ischemic conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aarts M, Iihara K, Wei WL, Xiong ZG, Arundine M, Cerwinski W, MacDonald JF, Tymianski M. A key role for TRPM7 channels in anoxic neuronal death. Cell. 2003;115:863–877. - PubMed
-
- Adlard PA, Cherny RA, Finkelstein DI, Gautier E, Robb E, Cortes M, Volitakis I, Liu X, Smith JP, Perez K, Laughton K, Li QX, Charman SA, Nicolazzo JA, Wilkins S, Deleva K, Lynch T, Kok G, Ritchie CW, Tanzi RE, Cappai R, Masters CL, Barnham KJ, Bush AI. Rapid restoration of cognition in Alzheimer's transgenic mice with 8-hydroxy quinoline analogs is associated with decreased interstitial Abeta. Neuron. 2008;59:43–55. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman E, Stout AK, Hartnett KA, Dineley KE, McLaughlin B, Reynolds IJ. Induction of neuronal apoptosis by thiol oxidation: putative role of intracellular zinc release. J Neurochem. 2000;75:1878–1888. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan WY, Chen Y, Swanson RA. Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama K, Watabe M, Nakaki T. Regulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;108:227–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
