Quorum sensing and a global regulator TsrA control expression of type VI secretion and virulence in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 21084635
- PMCID: PMC3000250
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1014998107
Quorum sensing and a global regulator TsrA control expression of type VI secretion and virulence in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
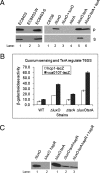
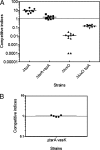
Vibrio cholerae is a human pathogen that causes the life-threatening diarrheal disease cholera. A type VI secretion system (T6SS) was recently shown to be required for full virulence in the O37 serogroup strain V52, which causes only sporadic human disease, but T6SS is not expressed in seventh pandemic O1 El Tor strains under standard laboratory conditions. In this study, we show that in the O1 El Tor strain C6706, T6SS is repressed by both quorum sensing and the uncharacterized protein VC0070 (TsrA). Disruption of TsrA and the quorum sensing regulator LuxO induces expression and secretion of the T6SS substrate Hcp, and this is dependent on the downstream regulator HapR, which directly binds to the promoter region of the T6SS genes hcp1 and hcp2 to induce expression. The activated T6SS in C6706 is functional and can translocate the effector protein VgrG-1 into macrophage cells, and T6SS activation leads to fecal diarrhea and intestinal inflammation in infant rabbits. Using an infant mouse infection model, we show that deletion of tsrA results in a 9.3-fold increase in intestinal colonization compared with wild type. TsrA functions as a global regulator to activate expression of hemagglutinin protease and repress cholera toxin and toxin coregulated pilus. Our findings provide significant insight into the molecular mechanism of T6SS and ToxT regulon gene regulation by quorum sensing and TsrA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

