1,2,3,4,6-Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose reduces renal crystallization and oxidative stress in a hyperoxaluric rat model
- PMID: 21085110
- PMCID: PMC4019041
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2010.458
1,2,3,4,6-Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose reduces renal crystallization and oxidative stress in a hyperoxaluric rat model
Abstract
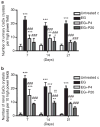
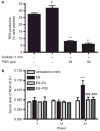
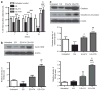
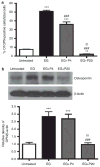
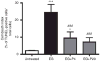
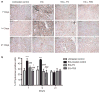
Adhesion of calcium oxalate (CaOx) crystals to kidney cells may be a key event in the pathogenesis of kidney stones associated with marked hyperoxaluria. Previously, we found that 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose (PGG), isolated from a traditional medicinal herb, reduced CaOx crystal adhesion to renal epithelial cells by acting on the cells as well as on the crystal surface. Here we used the ethylene glycol (EG)-mediated hyperoxaluric rat model and found evidence of oxidant stress as indicated by decreases in the activities of the renal antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, with increased kidney cell apoptosis and serum malondialdehyde levels, all evident by 21 days of EG treatment. These effects of hyperoxaluria were reversed by concurrent PGG treatment along with decreased urinary oxalate levels and CaOx supersaturation. Renal epithelial cell expression of the crystal binding molecule hyaluronan increased diffusely within 7 days of EG initiation, suggesting it is not a result of but precedes crystal deposition. Renal cell osteopontin (OPN) was also upregulated in EG-treated animals, and PGG significantly attenuated overexpression of both OPN and hyaluronan. Thus, our findings demonstrate that PGG reduces renal crystallization and oxidative renal cell injury, and may be a candidate chemopreventive agent for nephrolithiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gallotannin suppresses calcium oxalate crystal binding and oxalate-induced oxidative stress in renal epithelial cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(4):539-44. doi: 10.1248/bpb.35.539. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466558 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous extract of Boerhaavia diffusa root ameliorates ethylene glycol-induced hyperoxaluric oxidative stress and renal injury in rat kidney.Pharm Biol. 2011 Dec;49(12):1224-33. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2011.581671. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Pharm Biol. 2011. PMID: 21846174
-
Effect of angiotensin II receptor blockage on osteopontin expression and calcium oxalate crystal deposition in rat kidneys.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Mar;15(3):635-44. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000113321.49771.2d. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. PMID: 14978165
-
Nephrolithiasis: a consequence of renal epithelial cell exposure to oxalate and calcium oxalate crystals.Mol Urol. 2000 Winter;4(4):305-12. Mol Urol. 2000. PMID: 11156696 Review.
-
Calcium oxalate stone disease: role of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants.Urol Res. 2002 Mar;30(1):35-47. doi: 10.1007/s00240-001-0228-z. Urol Res. 2002. PMID: 11942324 Review.
Cited by
-
Gallotannin suppresses calcium oxalate crystal binding and oxalate-induced oxidative stress in renal epithelial cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(4):539-44. doi: 10.1248/bpb.35.539. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466558 Free PMC article.
-
Tannic acid, a higher galloylated pentagalloylglucose, suppresses antigen-specific IgE production by inhibiting ɛ germline transcription induced by STAT6 activation.FEBS Open Bio. 2013 Aug 5;3:341-5. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2013.07.008. eCollection 2013. FEBS Open Bio. 2013. PMID: 24251093 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation of hydrogen gas ameliorates glyoxylate-induced calcium oxalate deposition and renal oxidative stress in mice.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):2680-9. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045773 Free PMC article.
-
Triggering of suicidal erythrocyte death by penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Dec 24;6(1):54-65. doi: 10.3390/toxins6010054. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24368324 Free PMC article.
-
Biomolecular mechanism of urinary stone formation involving osteopontin.Urol Res. 2012 Dec;40(6):623-37. doi: 10.1007/s00240-012-0514-y. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Urol Res. 2012. PMID: 23124115 Review.
References
-
- Saita A, Bonaccorsi A, Motta M. Stone composition: where do we stand? Urol Int. 2007;79(Suppl 1):16–19. - PubMed
-
- Al-Ghamdi SS, Al-Ghamdi AA, Shammah AA. Inhibition of calcium oxalate nephrotoxicity with Cymbopogon schoenanthus (Al-Ethkher) Drug Metab Lett. 2007;1:241–244. - PubMed
-
- Yuliana ND, Khatib A, Link-Struensee AM, Ijzerman AP, et al. Adenosine A1 receptor binding activity of methoxy flavonoids from Orthosiphon stamineus. Planta Med. 2009;75:132–136. - PubMed
-
- Itoh Y, Yasui T, Okada A, Tozawa K, et al. Preventive effects of green tea on renal stone formation and the role of oxidative stress in nephrolithiasis. J Urol. 2005;173:271–275. - PubMed
-
- Jeong BC, Kim BS, Kim JI, Kim HH. Effects of green tea on urinary stone formation: an in vivo and in vitro study. J Endourol. 2006;20:356–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

