Hepatitis C virus (HCV) evades NKG2D-dependent NK cell responses through NS5A-mediated imbalance of inflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 21085608
- PMCID: PMC2978723
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001184
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) evades NKG2D-dependent NK cell responses through NS5A-mediated imbalance of inflammatory cytokines
Abstract
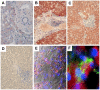
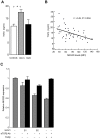
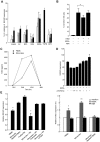
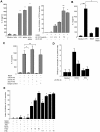
Understanding how hepatitis C virus (HCV) induces and circumvents the host's natural killer (NK) cell-mediated immunity is of critical importance in efforts to design effective therapeutics. We report here the decreased expression of the NKG2D activating receptor as a novel strategy adopted by HCV to evade NK-cell mediated responses. We show that chronic HCV infection is associated with expression of ligands for NKG2D, the MHC class I-related Chain (MIC) molecules, on hepatocytes. However, NKG2D expression is downmodulated on circulating NK cells, and consequently NK cell-mediated cytotoxic capacity and interferon-γ production are impaired. Using an endotoxin-free recombinant NS5A protein, we show that NS5A stimulation of monocytes through Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) promotes p38- and PI3 kinase-dependent IL-10 production, while inhibiting IL-12 production. In turn, IL-10 triggers secretion of TGFβ which downmodulates NKG2D expression on NK cells, leading to their impaired effector functions. Moreover, culture supernatants of HCV JFH1 replicating Huh-7.5.1 cells reproduce the effect of recombinant NS5A on NKG2D downmodulation. Exogenous IL-15 can antagonize the TGFβ effect and restore normal NKG2D expression on NK cells. We conclude that NKG2D-dependent NK cell functions are modulated during chronic HCV infection, and demonstrate that this alteration can be prevented by exogenous IL-15, which could represent a meaningful adjuvant for therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HBsAg stimulates NKG2D receptor expression on natural killer cells and inhibits hepatitis C virus replication.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018 Jun;17(3):233-240. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018. PMID: 29625837
-
Immunological changes in different patient populations with chronic hepatitis C virus infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 28;22(20):4848-59. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4848. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27239111 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired CD4⁺ T cell stimulation of NK cell anti-fibrotic activity may contribute to accelerated liver fibrosis progression in HIV/HCV patients.J Hepatol. 2013 Sep;59(3):427-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.029. Epub 2013 May 9. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665286
-
Chronic hepatitis C in the advanced adult and elderly subjects.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009 Jun;55(2):145-57. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009. PMID: 19305374 Review.
-
Natural killer cells: primary target for hepatitis C virus immune evasion strategies?Liver Transpl. 2006 Mar;12(3):363-72. doi: 10.1002/lt.20708. Liver Transpl. 2006. PMID: 16498647 Review.
Cited by
-
Role natural killer group 2D-ligand interactions in hepatitis B infection.World J Hepatol. 2015 Apr 28;7(6):819-24. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.819. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25937859 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Evasion of Natural Killer Cell Activation.Viruses. 2016 Apr 12;8(4):95. doi: 10.3390/v8040095. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27077876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of NK cells in fighting the virus infection and sepsis.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jul 22;18(14):3236-3248. doi: 10.7150/ijms.59898. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34400893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cells in liver disease.Hepatology. 2013 Apr;57(4):1654-62. doi: 10.1002/hep.26115. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23111952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver cirrhosis in HIV/HCV-coinfected individuals is related to NK cell dysfunction and exhaustion, but not to an impaired NK cell modulation by CD4+ T-cells.J Int AIDS Soc. 2019 Sep;22(9):e25375. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25375. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019. PMID: 31536177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raulet DH. Interplay of natural killer cells and their receptors with the adaptive immune response. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:996–1002. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Norris S, Collins C, Doherty DG, Smith F, McEntee G, et al. Resident human hepatic lymphocytes are phenotypically different from circulating lymphocytes. J Hepatol. 1998;28:84–90. - PubMed
-
- Khakoo SI, Thio CL, Martin MP, Brooks CR, Gao X, et al. HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science. 2004;305:872–874. - PubMed
-
- Golden-Mason L, Madrigal-Estebas L, McGrath E, Conroy MJ, Ryan EJ, et al. Altered natural killer cell subset distributions in resolved and persistent hepatitis C virus infection following single source exposure. Gut. 2008;57:1121–1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

