A coastal cline in sodium accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana is driven by natural variation of the sodium transporter AtHKT1;1
- PMID: 21085628
- PMCID: PMC2978683
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001193
A coastal cline in sodium accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana is driven by natural variation of the sodium transporter AtHKT1;1
Abstract
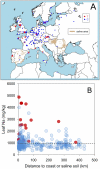
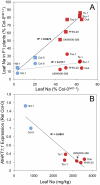
The genetic model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, like many plant species, experiences a range of edaphic conditions across its natural habitat. Such heterogeneity may drive local adaptation, though the molecular genetic basis remains elusive. Here, we describe a study in which we used genome-wide association mapping, genetic complementation, and gene expression studies to identify cis-regulatory expression level polymorphisms at the AtHKT1;1 locus, encoding a known sodium (Na(+)) transporter, as being a major factor controlling natural variation in leaf Na(+) accumulation capacity across the global A. thaliana population. A weak allele of AtHKT1;1 that drives elevated leaf Na(+) in this population has been previously linked to elevated salinity tolerance. Inspection of the geographical distribution of this allele revealed its significant enrichment in populations associated with the coast and saline soils in Europe. The fixation of this weak AtHKT1;1 allele in these populations is genetic evidence supporting local adaptation to these potentially saline impacted environments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Comment in
-
Beyond QTL cloning.PLoS Genet. 2010 Nov 11;6(11):e1001197. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001197. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21085636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilczek AM, Roe JL, Knapp MC, Lopez-Gallego C, Martin LJ, et al. Effects of genetic perturbation on seasonal life history plasticity. Science. 2009;323:930–934. - PubMed
-
- Paaby AB, Blacket MJ, Hoffmann AA, Schmidt PS. Identification of a candidate adaptive polymorphism for Drosophila life history by parallel independent clines on two continents. Mol Ecol. 2010;19:760–774. - PubMed
-
- McKechnie SW, Blacket MJ, Song SV, Rako L, Carroll X, et al. A clinally varying promoter polymorphism associated with adaptive variation in wing size in Drosophila. Mol Ecol. 2010;19:775–784. - PubMed
-
- Brady K, Kruckeberg A, Bradshaw HJ. Evolutionary ecology of plant adaptation to serpentine soils. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics. 2005;36:243–266.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

