Local gene regulation details a recognition code within the LacI transcriptional factor family
- PMID: 21085639
- PMCID: PMC2978694
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000989
Local gene regulation details a recognition code within the LacI transcriptional factor family
Abstract
The specific binding of regulatory proteins to DNA sequences exhibits no clear patterns of association between amino acids (AAs) and nucleotides (NTs). This complexity of protein-DNA interactions raises the question of whether a simple set of wide-coverage recognition rules can ever be identified. Here, we analyzed this issue using the extensive LacI family of transcriptional factors (TFs). We searched for recognition patterns by introducing a new approach to phylogenetic footprinting, based on the pervasive presence of local regulation in prokaryotic transcriptional networks. We identified a set of specificity correlations--determined by two AAs of the TFs and two NTs in the binding sites--that is conserved throughout a dominant subgroup within the family regardless of the evolutionary distance, and that act as a relatively consistent recognition code. The proposed rules are confirmed with data of previous experimental studies and by events of convergent evolution in the phylogenetic tree. The presence of a code emphasizes the stable structural context of the LacI family, while defining a precise blueprint to reprogram TF specificity with many practical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
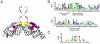
 in the sense strand of the palindromic combinations.
in the sense strand of the palindromic combinations.
 . We included the case for (AA-15, AA-16) = YQ corresponding to the synthetic SymL site in C). Recognition degeneracies are represented as unidirectional arrows (asymmetrical intrinsic), bidirectional divergent arrows (symmetrical intrinsic), and bidirectional convergent arrows (extrinsic). Colors for polar (green), basic (blue), acidic (red) and hydrophobic (black) amino acids. B) Agreement between synthetic and natural data. Recognition of (NT-5, NT-4)-palindromes by different (AA-15, AA-16)-LacI mutants (YQ is the wild type). Data from –from which we only considered those sequences (AA-15, AA-16) with a natural correspondence in Table S1. Rest of BS positions as in SymL. The larger the TF/BS affinity, the stronger the repression of the
. We included the case for (AA-15, AA-16) = YQ corresponding to the synthetic SymL site in C). Recognition degeneracies are represented as unidirectional arrows (asymmetrical intrinsic), bidirectional divergent arrows (symmetrical intrinsic), and bidirectional convergent arrows (extrinsic). Colors for polar (green), basic (blue), acidic (red) and hydrophobic (black) amino acids. B) Agreement between synthetic and natural data. Recognition of (NT-5, NT-4)-palindromes by different (AA-15, AA-16)-LacI mutants (YQ is the wild type). Data from –from which we only considered those sequences (AA-15, AA-16) with a natural correspondence in Table S1. Rest of BS positions as in SymL. The larger the TF/BS affinity, the stronger the repression of the  -galactosidase activity. Experimental conditions limited repression to a factor of 200. Arrows indicated again degeneracy classes. Predictions for wild type YQ correspond to asymmetric natural BSs (see text). (NT-5, NT-4)-palindromes involved in the predicted correlations for PM (
-galactosidase activity. Experimental conditions limited repression to a factor of 200. Arrows indicated again degeneracy classes. Predictions for wild type YQ correspond to asymmetric natural BSs (see text). (NT-5, NT-4)-palindromes involved in the predicted correlations for PM ( , see Table S1) lack an experimental test. Accordingly, PM do not exhibit a strong affinity for any of the tested palindromes (see Fig. S3), C) Natural and synthetic operators. A dot distinguishes the half sites. Flanking nucleotides separated by a space to help visualization of the highly conserved central region of the BSs. Colors identify different palindromic or mixed combinations in the specificity nucleotides (see Table S2 for more details).
, see Table S1) lack an experimental test. Accordingly, PM do not exhibit a strong affinity for any of the tested palindromes (see Fig. S3), C) Natural and synthetic operators. A dot distinguishes the half sites. Flanking nucleotides separated by a space to help visualization of the highly conserved central region of the BSs. Colors identify different palindromic or mixed combinations in the specificity nucleotides (see Table S2 for more details).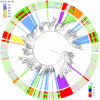
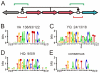
 binding to natural SymL-like BSs (Fig. 4.C and Table S2). Only one BS per TF is shown. The external color code displays the specificity-associated positions –to help visualization of palindromic combinations right positions are read in the complementary (c) strand:
binding to natural SymL-like BSs (Fig. 4.C and Table S2). Only one BS per TF is shown. The external color code displays the specificity-associated positions –to help visualization of palindromic combinations right positions are read in the complementary (c) strand:  . The color background in several branches corresponds to different recognition AAs (only a few recognition classes were enhanced). External color code in these branches shows darker colors to help visualization. Dots in branches denote bootstrap values larger than 80 (for 100 trees total, see Fig. S4 for more details).
. The color background in several branches corresponds to different recognition AAs (only a few recognition classes were enhanced). External color code in these branches shows darker colors to help visualization. Dots in branches denote bootstrap values larger than 80 (for 100 trees total, see Fig. S4 for more details).Similar articles
-
A generic approach to identify Transcription Factor-specific operator motifs; Inferences for LacI-family mediated regulation in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1.BMC Genomics. 2008 Mar 27;9:145. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-145. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18371204 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel evolution of ligand specificity between LacI/GalR family repressors and periplasmic sugar-binding proteins.Mol Biol Evol. 2003 Feb;20(2):267-77. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg038. Mol Biol Evol. 2003. PMID: 12598694
-
Anti-correlation of LacI association and dissociation rates observed in living cells.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 17;16(1):764. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56053-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39824877 Free PMC article.
-
Lactose repressor protein: functional properties and structure.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998;58:127-64. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60035-5. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9308365 Review.
-
Phylogenetic, structural and functional analyses of the LacI-GalR family of bacterial transcription factors.FEBS Lett. 1995 Dec 18;377(2):98-102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01344-x. FEBS Lett. 1995. PMID: 8543068 Review.
Cited by
-
IpsA, a novel LacI-type regulator, is required for inositol-derived lipid formation in Corynebacteria and Mycobacteria.BMC Biol. 2013 Dec 30;11:122. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-11-122. BMC Biol. 2013. PMID: 24377418 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Position-Specific Correlations between DNA-Binding Domains and Their Binding Sites. Application to the MerR Family of Transcription Factors.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 30;11(9):e0162681. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162681. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27690309 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping DNA sequence to transcription factor binding energy in vivo.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Feb 4;15(2):e1006226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006226. eCollection 2019 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 30716072 Free PMC article.
-
The LacI-Type transcriptional regulator AraR acts as an L-arabinose-responsive repressor of L-arabinose utilization genes in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 31831.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jun;196(12):2242-54. doi: 10.1128/JB.01655-14. Epub 2014 Apr 4. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24706742 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Streptococcus mutans PTS Bio by the transcriptional repressor NigR.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2015 Aug;30(4):280-94. doi: 10.1111/omi.12093. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25580872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pabo CO, Sauer RT. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki M, Brenner SE, Gerstein M, Yagi N. DNA recognition code of transcription factors. Protein Eng Des Sel. 1995;8:319–328. - PubMed
-
- Choo Y, Klug A. Physical basis of a protein-DNA recognition code. Current Opinion In Struct Biol. 1997;7:117–125. - PubMed

