Inhibition of endothelin-1-mediated contraction of hepatic stellate cells by FXR ligand
- PMID: 21085652
- PMCID: PMC2978707
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013955
Inhibition of endothelin-1-mediated contraction of hepatic stellate cells by FXR ligand
Abstract
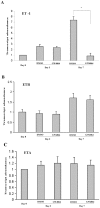
Activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) plays an important role in the development of cirrhosis through the increased production of collagen and the enhanced contractile response to vasoactive mediators such as endothelin-1 (ET-1). The farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily that is highly expressed in liver, kidneys, adrenals, and intestine. FXR is also expressed in HSCs and activation of FXR in HSCs is associated with significant decreases in collagen production. However, little is known about the roles of FXR in the regulation of contraction of HSCs. We report in this study that treatment of quiescent HSCs with GW4064, a synthetic FXR agonist, significantly inhibited the HSC transdifferentiation, which was associated with an inhibition of the upregulation of ET-1 expression. These GW4064-treated cells also showed reduced contractile response to ET-1 in comparison to HSCs without GW4064 treatment. We have further shown that GW4064 treatment inhibited the ET-1-mediated contraction in fully activated HSCs. To elucidate the potential mechanism we showed that GW4064 inhibited ET-1-mediated activation of Rho/ROCK pathway in activated HSCs. Our studies unveiled a new mechanism that might contribute to the anti-cirrhotic effects of FXR ligands.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




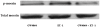
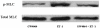
References
-
- Blomhoff R, Wake K. Perisinusoidal stellate cells of the liver: important roles in retinol metabolism and fibrosis. FASEB J. 1991;5:271–277. - PubMed
-
- Rockey DC, Weisiger RA. Endothelin induced contractility of stellate cells from normal and cirrhotic rat liver: implications for regulation of portal pressure and resistance. Hepatology. 1996;24:233–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

