Amyloid-β oligomer specificity mediated by the IgM isotype--implications for a specific protective mechanism exerted by endogenous auto-antibodies
- PMID: 21085663
- PMCID: PMC2978096
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013928
Amyloid-β oligomer specificity mediated by the IgM isotype--implications for a specific protective mechanism exerted by endogenous auto-antibodies
Abstract
Background: Alzheimers disease (AD) has been strongly linked to an anomalous self-assembly of the amyloid-β peptide (Aβ). The correlation between clinical symptoms of AD and Aβ depositions is, however, weak. Instead small and soluble Aβ oligomers are suggested to exert the major pathological effects. In strong support of this notion, immunological targeting of Aβ oligomers in AD mice-models shows that memory impairments can be restored without affecting the total burden of Aβ deposits. Consequently a specific immunological targeting of Aβ oligomers is of high therapeutic interest.
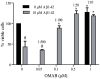
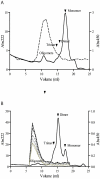
Methodology/principal findings: Previously the generation of conformational-dependent oligomer specific anti-Aβ antibodies has been described. However, to avoid the difficult task of identifying a molecular architecture only present on oligomers, we have focused on a more general approach based on the hypothesis that all oligomers expose multiple identical epitopes and therefore would have an increased binding to a multivalent receptor. Using the polyvalent IgM immunoglobulin we have developed a monoclonal anti-Aβ antibody (OMAB). OMAB only demonstrates a weak interaction with Aβ monomers and dimers having fast on and off-rate kinetics. However, as an effect of avidity, its interaction with Aβ-oligomers results in a strong complex with an exceptionally slow off-rate. Through this mechanism a selectivity towards Aβ oligomers is acquired and OMAB fully inhibits the cytotoxic effect exerted by Aβ(1-42) at highly substoichiometric ratios. Anti-Aβ auto-antibodies of IgM isotype are frequently present in the sera of humans. Through a screen of endogenous anti-Aβ IgM auto-antibodies from a group of healthy individuals we show that all displays a preference for oligomeric Aβ.
Conclusions/significance: Taken together we provide a simple and general mechanism for targeting of oligomers without the requirement of conformational-dependent epitopes. In addition, our results suggest that IgM anti-Aβ auto-antibodies may exert a more specific protective mechanism in vivo than previously anticipated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Restricted V gene usage and VH/VL pairing of mouse humoral response against the N-terminal immunodominant epitope of the amyloid β peptide.Mol Immunol. 2010 Nov-Dec;48(1-3):59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.09.012. Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20970857 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the β-amyloid(4-10) epitope of plaque specific Aβ antibodies by affinity-mass spectrometry using alanine site mutation.J Pept Sci. 2018 Jan;24(1). doi: 10.1002/psc.3047. J Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 29322650
-
The binding affinity of anti-Aβ1-42 MAb-decorated nanoliposomes to Aβ1-42 peptides in vitro and to amyloid deposits in post-mortem tissue.Biomaterials. 2011 Aug;32(23):5489-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.020. Epub 2011 May 6. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21529932
-
The Role of Amyloid-β Oligomers in Toxicity, Propagation, and Immunotherapy.EBioMedicine. 2016 Apr;6:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.03.035. Epub 2016 Apr 5. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27211547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformation-specific antibodies to target amyloid β oligomers and their application to immunotherapy for Alzheimer's disease.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;78(8):1293-305. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2014.940275. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25130729 Review.
Cited by
-
Human LilrB2 is a β-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer's model.Science. 2013 Sep 20;341(6152):1399-404. doi: 10.1126/science.1242077. Science. 2013. PMID: 24052308 Free PMC article.
-
Single-protein nanomechanical mass spectrometry in real time.Nat Nanotechnol. 2012 Sep;7(9):602-8. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.119. Epub 2012 Aug 26. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22922541 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histidines in amyloid β fibril assembly.FEBS Lett. 2017 Apr;591(8):1167-1175. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12616. Epub 2017 Apr 3. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28267202 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease: the potential therapeutic role of the natural antibiotic amyloid-β peptide.Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2016 Oct;6(5):345-8. doi: 10.2217/nmt-2016-0035. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2016. PMID: 27599536 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The anti-cancer IgM monoclonal antibody PAT-SM6 binds with high avidity to the unfolded protein response regulator GRP78.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044927. Epub 2012 Sep 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwatsubo T, Odaka A, Suzuki N, Mizusawa H, Nukina N, et al. Visualization of A beta 42(43) and A beta 40 in senile plaques with end-specific A beta monoclonals: evidence that an initially deposited species is A beta 42(43). Neuron. 1994;13:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Katzman R. Differential diagnosis of dementing illnesses. Neurol Clin. 1986;4:329–340. - PubMed
-
- Morgan D, Diamond DM, Gottschall PE, Ugen KE, Dickey C, et al. A beta peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2000;408:982–985. - PubMed
-
- Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W, Gordon G, Grajeda H, et al. Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature. 1999;400:173–177. - PubMed
-
- Younkin SG. Amyloid beta vaccination: reduced plaques and improved cognition. Nat Med. 2001;7:18–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

