Phenotypic complexity, measurement bias, and poor phenotypic resolution contribute to the missing heritability problem in genetic association studies
- PMID: 21085666
- PMCID: PMC2978099
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013929
Phenotypic complexity, measurement bias, and poor phenotypic resolution contribute to the missing heritability problem in genetic association studies
Abstract
Background: The variance explained by genetic variants as identified in (genome-wide) genetic association studies is typically small compared to family-based heritability estimates. Explanations of this 'missing heritability' have been mainly genetic, such as genetic heterogeneity and complex (epi-)genetic mechanisms.
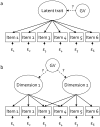
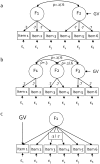
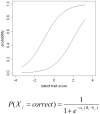
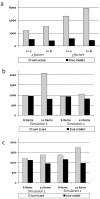
Methodology: We used comprehensive simulation studies to show that three phenotypic measurement issues also provide viable explanations of the missing heritability: phenotypic complexity, measurement bias, and phenotypic resolution. We identify the circumstances in which the use of phenotypic sum-scores and the presence of measurement bias lower the power to detect genetic variants. In addition, we show how the differential resolution of psychometric instruments (i.e., whether the instrument includes items that resolve individual differences in the normal range or in the clinical range of a phenotype) affects the power to detect genetic variants.
Conclusion: We conclude that careful phenotypic data modelling can improve the genetic signal, and thus the statistical power to identify genetic variants by 20-99%.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Li J, Coates RJ, Gwinn M, Khoury MJ. Steroid 5-α-Reductase Type 2 (SRD5a2) gene polymorphism and risk of prostate cancer: a HuGE review Human Genome. Epidemiology. 2010;171:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Peng B, Cao L, Wang W, Xian L, Jiang D, et al. Polymorphisms in the promotor region of matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 3 cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 50 case-control studies. Mutagenesis. 2010;25:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Tian Y, Li Y, Hu Z, Wang D, Sum X, et al. Differential effects of NOD2 polymorphisms on colorectal cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2010;25:161–168. - PubMed
-
- Zhang HF, Qiu LX, Chen Y, Zu WL, Mao C, et al. ATG16L1 T300A polymorphism and Crohn's disease susceptibility: evidence from 13022 cases and 17532 controls. Hum Gen. 2009;125:627–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

