Induction of glucose metabolism in stimulated T lymphocytes is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
- PMID: 21085672
- PMCID: PMC2978105
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015425
Induction of glucose metabolism in stimulated T lymphocytes is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
Abstract
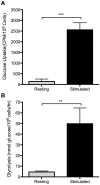
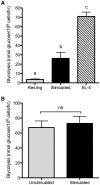
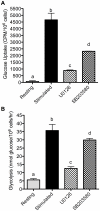
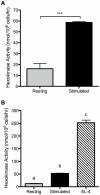
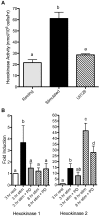
T lymphocytes play a critical role in cell-mediated immune responses. During activation, extracellular and intracellular signals alter T cell metabolism in order to meet the energetic and biosynthetic needs of a proliferating, active cell, but control of these phenomena is not well defined. Previous studies have demonstrated that signaling from the costimulatory receptor CD28 enhances glucose utilization via the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway. However, since CD28 ligation alone does not induce glucose metabolism in resting T cells, contributions from T cell receptor-initiated signaling pathways must also be important. We therefore investigated the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling in the regulation of mouse T cell glucose metabolism. T cell stimulation strongly induces glucose uptake and glycolysis, both of which are severely impaired by inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), whereas p38 inhibition had a much smaller effect. Activation also induced hexokinase activity and expression in T cells, and both were similarly dependent on ERK signaling. Thus, the ERK signaling pathway cooperates with PI3K to induce glucose utilization in activated T cells, with hexokinase serving as a potential point for coordinated regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cooper EH, Barkhan P, Hale AJ. Observations on the Proliferation of Human Leucocytes Cultured with Phytohaemagglutinin. Brit J Haemat. 1963;9:101–111. - PubMed
-
- Roos D, Loos JA. Changes in the carbohydrate metabolism of mitogenically stimulated human peripheral lymphocytes. I. Stimulation by phytohaemagglutinin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;222:565–582. - PubMed
-
- Sagone AL, Jr, LoBuglio AF, Balcerzak SP. Alterations in hexose monophosphate shunt during lymphoblastic transformation. Cell Immunol. 1974;14:443–452. - PubMed
-
- Culvenor JG, Weidemann MJ. Phytohaemagglutinin stimulation of rat thymus lymphocytes glycolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976;437:354–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

