Expansion and characterization of human melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)
- PMID: 21085676
- PMCID: PMC2978109
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013940
Expansion and characterization of human melanoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)
Abstract
Background: Various immunotherapeutic strategies for cancer are aimed at augmenting the T cell response against tumor cells. Adoptive cell therapy (ACT), where T cells are manipulated ex vivo and subsequently re-infused in an autologous manner, has been performed using T cells from various sources. Some of the highest clinical response rates for metastatic melanoma have been reported in trials using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). These protocols still have room for improvement and furthermore are currently only performed at a limited number of institutions. The goal of this work was to develop TILs as a therapeutic product at our institution.
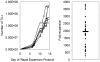
Principal findings: TILs from 40 melanoma tissue specimens were expanded and characterized. Under optimized culture conditions, 72% of specimens yielded rapidly proliferating TILs as defined as at least one culture reaching ≥3×10(7) TILs within 4 weeks. Flow cytometric analyses showed that cultures were predominantly CD3+ T cells, with highly variable CD4+:CD8+ T cell ratios. In total, 148 independent bulk TIL cultures were assayed for tumor reactivity. Thirty-four percent (50/148) exhibited tumor reactivity based on IFN-γ production and/or cytotoxic activity. Thirteen percent (19/148) showed specific cytotoxic activity but not IFN-γ production and only 1% (2/148) showed specific IFN-γ production but not cytotoxic activity. Further expansion of TILs using a 14-day "rapid expansion protocol" (REP) is required to induce a 500- to 2000-fold expansion of TILs in order to generate sufficient numbers of cells for current ACT protocols. Thirty-eight consecutive test REPs were performed with an average 1865-fold expansion (+/- 1034-fold) after 14 days.
Conclusions: TILs generally expanded efficiently and tumor reactivity could be detected in vitro. These preclinical data from melanoma TILs lay the groundwork for clinical trials of ACT.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, et al. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature. 2001;410:1107–1111. - PubMed
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity. 2004;21:137–148. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami Y, Dang N, Wang X, Tupesis J, Robbins PF, et al. Recognition of shared melanoma antigens in association with major HLA-A alleles by tumor infiltrating T lymphocytes from 123 patients with melanoma. J Immunother. 2000;23:17–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

