α-actinin-4 is essential for maintaining the spreading, motility and contractility of fibroblasts
- PMID: 21085685
- PMCID: PMC2978680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013921
α-actinin-4 is essential for maintaining the spreading, motility and contractility of fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: α-Actinins cross-link actin filaments, with this cross-linking activity regulating the formation of focal adhesions, intracellular tension, and cell migration. Most non-muscle cells such as fibroblasts express two isoforms, α-actinin-1 (ACTN1) and α-actinin-4 (ACTN4). The high homology between these two isoforms would suggest redundancy of their function, but recent studies have suggested different regulatory roles. Interestingly, ACTN4 is phosphorylated upon growth factor stimulation, and this loosens its interaction with actin.
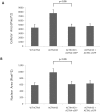
Methodology/principal findings: Using molecular, biochemical and cellular techniques, we probed the cellular functions of ACTN4 in fibroblasts. Knockdown of ACTN4 expression in murine lung fibroblasts significantly impaired cell migration, spreading, adhesion, and proliferation. Surprisingly, knockdown of ACTN4 enhanced cellular compaction and contraction force, and increased cellular and nuclear cross-sectional area. These results, except the increased contractility, are consistent with a putative role of ACTN4 in cytokinesis. For the transcellular tension, knockdown of ACTN4 significantly increased the expression of myosin light chain 2, a element of the contractility machinery. Re-expression of wild type human ACTN4 in ACTN4 knockdown murine lung fibroblasts reverted cell spreading, cellular and nuclear cross-sectional area, and contractility back towards baseline, demonstrating that the defect was due to absence of ACTN4.
Significance: These results suggest that ACTN4 is essential for maintaining normal spreading, motility, cellular and nuclear cross-sectional area, and contractility of murine lung fibroblasts by maintaining the balance between transcellular contractility and cell-substratum adhesion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
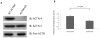




References
-
- Otey CA, Carpen O. Alpha-actinin revisited: a fresh look at an old player. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2004;58:104–111. - PubMed
-
- Quick Q, Skalli O. Alpha-actinin 1 and alpha-actinin 4: contrasting roles in the survival, motility, and RhoA signaling of astrocytoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316:1137–1147. - PubMed
-
- Michaud JL, Hosseini-Abardeh M, Farah K, Kennedy CR. Modulating alpha-actinin-4 dynamics in podocytes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009;66:166–178. - PubMed
-
- Honda K, Yamada T, Hayashida Y, Idogawa M, Sato S, et al. Actinin-4 increases cell motility and promotes lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:51–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

