Proximal humerus reconstruction after tumour resection: biological versus endoprosthetic reconstruction
- PMID: 21085956
- PMCID: PMC3167452
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-010-1152-z
Proximal humerus reconstruction after tumour resection: biological versus endoprosthetic reconstruction
Abstract
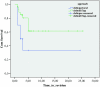
The purpose of this study was to compare the outcome, complications and survival of the three most commonly used surgical reconstructions of the proximal humerus after transarticular tumour resection. Between 1985 and 2005, 38 consecutive proximal humeral reconstructions using allograft-prosthesis composite (n = 10), osteoarticular allograft (n = 13) or a modular tumour prosthesis (n = 14) were performed in our clinic. The mean follow-up was ten years (1-25). Of these, 27 were disease free at latest follow-up (mean 16.8 years) and ten had died of disease. The endoprosthetic group presented the smallest complication rate of 21% (n =1), compared to 40% (n = 4) in the allograft-prosthesis composite and 62% (n = 8) in the osteoarticular allograft group. Only one revision was performed in the endoprosthetic group, in a case of shoulder instability. Infection after revision (n = 3), pseudoarthrosis (n = 2), fracture of the allograft (n = 3) and shoulder instability (n = 4) were the major complications of allograft use in general. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a significantly better implant survival for the endoprosthetic group (log-rank p = 0.002). At final follow-up the Musculoskeletal Tumour Society scores were an average of 72% for the allograft-prosthetic composite (n = 7, median follow-up 17 years), 76% for the osteoarticular allograft (n = 3, 19 years) and 77% for the endoprosthetic reconstruction (n = 10, 5 years) groups. An endoprosthetic reconstruction after transarticular proximal humeral resection resulted in the lowest complication rate, highest implant survival and comparable functional results when compared to allograft-prosthesis composite and osteoarticular allograft use. We believe that the surgical approach that best preserves the abductor mechanism and provides sufficient surgical exposure for tumour resection contributed to better functional results and glenohumeral stability in the endoprosthetic group.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proximal humerus reconstructions for tumors.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009 Apr;467(4):1035-41. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0531-x. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. PMID: 18820983 Free PMC article.
-
Allograft-prosthesis composite reconstruction of the proximal part of the humerus: surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Sep;92 Suppl 1 Pt 2:188-96. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00167. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010. PMID: 20844174
-
Proximal Tibia Reconstruction After Bone Tumor Resection: Are Survivorship and Outcomes of Endoprosthetic Replacement and Osteoarticular Allograft Similar?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Mar;475(3):676-682. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4843-y. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27103142 Free PMC article.
-
Malawer type I/V proximal humerus reconstruction after tumor resection: a systematic review.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 Sep;33(9):2096-2108. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2024.03.015. Epub 2024 Apr 19. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 38642876
-
Proximal Tibial Reconstruction After Tumor Resection: A Systematic Review of the Literature.JBJS Rev. 2019 Jul;7(7):e1. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.18.00146. JBJS Rev. 2019. PMID: 31268862
Cited by
-
[Bone defect reconstruction in bone sarcoma surgery: tumour endoprosthesis versus biological reconstruction].Unfallchirurg. 2014 Jul;117(7):600-6. doi: 10.1007/s00113-013-2476-0. Unfallchirurg. 2014. PMID: 25030959 German.
-
Endoprosthetic reconstruction of the proximal humerus after tumour resection with polypropylene mesh.Int Orthop. 2015 Mar;39(3):501-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-014-2597-2. Epub 2014 Nov 23. Int Orthop. 2015. PMID: 25416123
-
Additively manufactured patient-specific prosthesis for tumor reconstruction: Design, process, and properties.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 14;16(7):e0253786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253786. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34260623 Free PMC article.
-
Osteosarcoma: prognosis plateau warrants retinoblastoma pathway targeted therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016 Mar 25;1:16001. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2016.1. eCollection 2016. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016. PMID: 29263893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reverse Allograft Prosthetic-Composite Versus Endoprosthesis Reconstruction for Massive Proximal Humerus Bone Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Outcomes and Complications.Indian J Orthop. 2024 Sep 1;58(10):1339-1348. doi: 10.1007/s43465-024-01248-7. eCollection 2024 Oct. Indian J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39324078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical