Calcium-induced cleavage of DNA topoisomerase I involves the cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling of calpain 2
- PMID: 21086148
- PMCID: PMC11114693
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0591-4
Calcium-induced cleavage of DNA topoisomerase I involves the cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling of calpain 2
Abstract
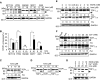
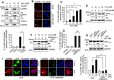
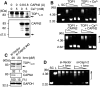
Important to the function of calpains is temporal and spatial regulation of their proteolytic activity. Here, we demonstrate that cytoplasm-resident calpain 2 cleaves human nuclear topoisomerase I (hTOP1) via Ca(2+)-activated proteolysis and nucleoplasmic shuttling of proteases. This proteolysis of hTOP1 was induced by either ionomycin-caused Ca(2+) influx or addition of Ca(2+) in cellular extracts. Ca(2+) failed to induce hTOP1 proteolysis in calpain 2-knockdown cells. Moreover, calpain 2 cleaved hTOP1 in vitro. Furthermore, calpain 2 entered the nucleus upon Ca(2+) influx, and calpastatin interfered with this process. Calpain 2 cleavage sites were mapped at K(158) and K(183) of hTOP1. Calpain 2-truncated hTOP1 exhibited greater relaxation activity but remained able to interact with nucleolin and to form cleavable complexes. Interestingly, calpain 2 appears to be involved in ionomycin-induced protection from camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity. Thus, our data suggest that nucleocytoplasmic shuttling may serve as a novel type of regulation for calpain 2-mediated nuclear proteolysis.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

