Sensitivity of beamformer source analysis to deficiencies in forward modeling
- PMID: 21086549
- PMCID: PMC6871065
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20986
Sensitivity of beamformer source analysis to deficiencies in forward modeling
Abstract
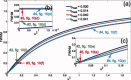
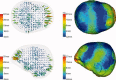
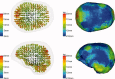
Beamforming approaches have recently been developed for the field of electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) source analysis and opened up new applications within various fields of neuroscience. While the number of beamformer applications thus increases fast-paced, fundamental methodological considerations, especially the dependence of beamformer performance on leadfield accuracy, is still quite unclear. In this article, we present a systematic study on the influence of improper volume conductor modeling on the source reconstruction performance of an EEG-data based synthetic aperture magnetometry (SAM) beamforming approach. A finite element model of a human head is derived from multimodal MR images and serves as a realistic volume conductor model. By means of a theoretical analysis followed by a series of computer simulations insight is gained into beamformer performance with respect to reconstruction errors in peak location, peak amplitude, and peak width resulting from geometry and anisotropy volume conductor misspecifications, sensor noise, and insufficient sensor coverage. We conclude that depending on source position, sensor coverage, and accuracy of the volume conductor model, localization errors up to several centimeters must be expected. As we could show that the beamformer tries to find the best fitting leadfield (least squares) with respect to its scanning space, this result can be generalized to other localization methods. More specific, amplitude, and width of the beamformer peaks significantly depend on the interaction between noise and accuracy of the volume conductor model. The beamformer can strongly profit from a high signal-to-noise ratio, but this requires a sufficiently realistic volume conductor model.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



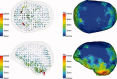

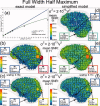
References
-
- Baillet S, Mosher JC, Leahy RM ( 2001): Electromagnetic brain mapping. IEEE Signal Process Mag 18: 14–30.
-
- Bertrand O, Thévenet M, Perrin F ( 1991): 3D finite element method in brain electrical activity studies In: Nenoner J, Rajala HM, Katila T, editors. Biomagnetic Localization and 3D Modelling. Helsinki University of Technology, Helsinki, pp 154–171.
-
- Brookes MJ, Gibson AM, Hall SD, Furlong PL, Barnes GR, Hillebrand A, Singh KD, Holliday IE, Francis ST, Morris PG ( 2004): A general linear model for MEG beamformer imaging. Neuroimage 23: 936–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

