One life ends, another begins: Management of a brain-dead pregnant mother-A systematic review-
- PMID: 21087498
- PMCID: PMC3002294
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-74
One life ends, another begins: Management of a brain-dead pregnant mother-A systematic review-
Abstract
Background: An accident or a catastrophic disease may occasionally lead to brain death (BD) during pregnancy. Management of brain-dead pregnant patients needs to follow special strategies to support the mother in a way that she can deliver a viable and healthy child and, whenever possible, also be an organ donor. This review discusses the management of brain-dead mothers and gives an overview of recommendations concerning the organ supporting therapy.
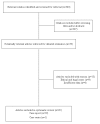
Methods: To obtain information on brain-dead pregnant women, we performed a systematic review of Medline, EMBASE and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL). The collected data included the age of the mother, the cause of brain death, maternal medical complications, gestational age at BD, duration of extended life support, gestational age at delivery, indication of delivery, neonatal outcome, organ donation of the mothers and patient and graft outcome.
Results: In our search of the literature, we found 30 cases reported between 1982 and 2010. A nontraumatic brain injury was the cause of BD in 26 of 30 mothers. The maternal mean age at the time of BD was 26.5 years. The mean gestational age at the time of BD and the mean gestational age at delivery were 22 and 29.5 weeks, respectively. Twelve viable infants were born and survived the neonatal period.
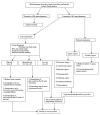
Conclusion: The management of a brain-dead pregnant woman requires a multidisciplinary team which should follow available standards, guidelines and recommendations both for a nontraumatic therapy of the fetus and for an organ-preserving treatment of the potential donor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
-
Maternal and neonatal outcomes of elective induction of labor.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009 Mar;(176):1-257. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009. PMID: 19408970 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics for treating gonorrhoea in pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 21;2(2):CD011167. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011167.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29465747 Free PMC article.
-
Planned early birth versus expectant management for women with preterm prelabour rupture of membranes prior to 37 weeks' gestation for improving pregnancy outcome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 3;3(3):CD004735. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004735.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28257562 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 06;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. PMID: 17253490 Updated.
Cited by
-
Brain death and care of the organ donor.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Apr-Jun;32(2):146-52. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.168266. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27275040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryonics, euthanasia, and the doctrine of double effect.Philos Ethics Humanit Med. 2023 Jun 29;18(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13010-023-00137-5. Philos Ethics Humanit Med. 2023. PMID: 37381023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do the 'brain dead' merely appear to be alive?J Med Ethics. 2017 Nov;43(11):747-753. doi: 10.1136/medethics-2016-103867. Epub 2017 Aug 28. J Med Ethics. 2017. PMID: 28848063 Free PMC article.
-
Critical care in obstetrics.Indian J Anaesth. 2018 Sep;62(9):724-733. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_577_18. Indian J Anaesth. 2018. PMID: 30237599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A brain-dead pregnant woman with prolonged somatic support and successful neonatal outcome: A grand rounds case with a detailed review of literature and ethical considerations.Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2013 Jul;3(3):220-4. doi: 10.4103/2229-5151.119205. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2013. PMID: 24404463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mollaret P, Goulon M. Le coma dépassé. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1959;101:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Suddaby EC, Schaeffer MJ, Brigham LE, Shaver TR. Analysis of organ donors in the peripartum period. J Transpl Coord. 1998;8:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Holmquist M, Chabalewski F, Blount T, Edwards C, McBride V, Pietroski R. A critical pathway: guiding care for organ donors. Crit Care Nurse. 1999;19:84–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical