Efficacy of postural techniques assessed by videofluoroscopy for myasthenia gravis with dysphagia as the presenting symptom: a case report
- PMID: 21087522
- PMCID: PMC3009659
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-370
Efficacy of postural techniques assessed by videofluoroscopy for myasthenia gravis with dysphagia as the presenting symptom: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Oropharyngeal weakness leading to dysphagia is rarely the presenting symptom of myasthenia gravis, but it can be a significant source of morbidity and mortality. The earliest possible diagnosis of myasthenia gravis should be made for better management of this cause of treatable dysphagia. A detailed evaluation of swallowing by videofluoroscopy can assist in making an accurate diagnosis and in individualizing appropriate diet compensatory techniques.
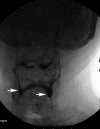
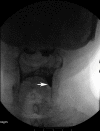
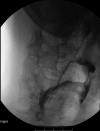
Case presentation: We present the case of a 57-year-old Taiwanese man with dysphagia as the presenting symptom of myasthenia gravis, and evaluate the pathological findings of swallowing and effectiveness of compensatory postural techniques for dysphagia using videofluoroscopy.
Conclusions: Videofluoroscopy is a valuable technique for evaluating myasthenia gravis dysphagia, because it allows swallowing interventions to be precisely individualized in accordance with the results obtained.
Figures
References
-
- Thomas CE, Mayer SA, Gungor Y, Swarup R, Webster EA, Chang I, Brannagan TH, Fink ME, Rowland LP. Myasthenic crisis: clinical features, mortality, complications, and risk factors for prolonged intubation. Neurology. 1997;48:1253–1260. - PubMed
-
- Palmer JB, Monahan DM, Matsuo K. In: Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 3. Braddom RL, editor. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Inc; 2007. Rehabilitation of patients with swallowing disorders; pp. 597–616.
-
- Huang MH, King KL, Chien KY. Esophageal manometric studies in patients with myasthenia gravis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1988;95:281–285. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

