Death by releasing the breaks: CHK1 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 21087899
- PMCID: PMC6905465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.10.009
Death by releasing the breaks: CHK1 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics
Abstract
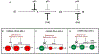
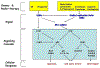
Defects in p53 function, which occur frequently in human cancers due to mutations in TP53 or disruptions in the p53 regulatory pathway, render cells dependent on CHK1 (Checkpoint Kinase 1) to activate cell cycle checkpoints. In the presence of DNA damage or replication stress, inhibition of CHK1 leads to "mitotic catastrophe" and cell death in p53-deficient tumors while sparing p53-proficient cells. CHK1 inhibitors sensitize tumors to a variety of DNA-damaging agents or antimetabolites in preclinical models and are being evaluated in early phase clinical trials. In this review, we summarize recent advances and controversies in the development and application of CHK1 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Schlegel R, and Pardee AB (1986) Caffeine-induced uncoupling of mitosis from the completion of DNA replication in mammalian cells. Science 232, 1264–1266 - PubMed
-
- Fan S, et al. (1995) Disruption of p53 function sensitizes breast cancer MCF-7 cells to cisplatin and pentoxifylline. Cancer Res 55, 1649–1654 - PubMed
-
- Powell SN, et al. (1995) Differential Sensitivity of p53(−) and p53(+) cells to caffeine-induced radiosensitization and override of G2 delay. Cancer Research 55, 1643–1648 - PubMed
-
- Russell KJ, et al. (1995) Abrogation of the G2 checkpoint results in differential radiosensitization of G1 checkpoint-deficient and G1 checkpoint-competent cells. Cancer Res 55, 1639–1642 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

