A p27(kip1)-binding protein, p27RF-Rho, promotes cancer metastasis via activation of RhoA and RhoC
- PMID: 21087931
- PMCID: PMC3024806
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.159715
A p27(kip1)-binding protein, p27RF-Rho, promotes cancer metastasis via activation of RhoA and RhoC
Abstract
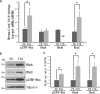
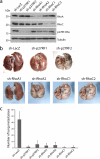
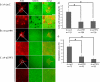
Rho family proteins regulate multiple cellular functions including motility and invasion through regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and gene expression. Activation of Rho proteins is controlled precisely by multiple regulators in a spatiotemporal manner. RhoA and/or RhoC are key players that regulate the metastatic activity of malignant tumor cells, and it is therefore of particular interest to understand how activation of these Rho proteins is controlled. We recently identified an upstream regulator of RhoA activation, p27RF-Rho (p27(kip1) releasing factor from RhoA) that acts by freeing RhoA from inhibition by p27(kip1). p27(kip1) is a cell cycle regulator when it is localized to the nucleus, but it binds RhoA and inhibits activation of the latter when it is localized to the cytoplasm. Here, we show that a metastatic variant of mouse melanoma B16 cells (F10) exhibits greater expression of p27RF-Rho, RhoA, and RhoC than the nonmetastatic parental cells (F0). Injection of F10 cells into mouse tail vein resulted in the formation of metastatic lung colonies, whereas prior knockdown of expression of either one of the three proteins using specific shRNA sequences decreased metastasis markedly. p27RF-Rho regulated the activation of RhoA and RhoC and thereby modulated cellular adhesion and motility, in addition to pericellular proteolysis. The Rho activities enhanced by p27RF-Rho had a marked effect upon efficiency of lodging of F10 cells in the lung, which represents an early step of metastasis. p27RF-Rho also regulated metastasis of human melanoma and fibrosarcoma cells. Thus, p27RF-Rho is a key upstream regulator of RhoA and RhoC that controls spreading of tumor cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel protein associated with membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase binds p27(kip1) and regulates RhoA activation, actin remodeling, and matrigel invasion.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 2;284(40):27315-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041400. Epub 2009 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19654316 Free PMC article.
-
A novel strategy for specifically down-regulating individual Rho GTPase activity in tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 7;278(45):44617-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308929200. Epub 2003 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12939257
-
The interaction between caveolin-1 and Rho-GTPases promotes metastasis by controlling the expression of alpha5-integrin and the activation of Src, Ras and Erk.Oncogene. 2012 Feb 16;31(7):884-96. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.288. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21765460 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA, RhoB and RhoC have different roles in cancer cell migration.J Microsc. 2013 Sep;251(3):242-9. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12025. Epub 2013 Mar 12. J Microsc. 2013. PMID: 23488932 Review.
-
Why three Rho proteins? RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, and cell motility.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Nov 15;301(1):43-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.012. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15501444 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-493 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting RhoC.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Oct;18(10):1027-33. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26730339 Free PMC article.
-
Geranylgeranyltransferase I promotes human glioma cell growth through Rac1 membrane association and activation.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Jan;49(1):130-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9905-3. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23073905
-
Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of P27RF-Rho inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2017;21(1):35-41. doi: 10.5114/wo.2017.66654. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2017. PMID: 28435396 Free PMC article.
-
Control of metastatic niche formation by targeting APBA3/Mint3 in inflammatory monocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 May 30;114(22):E4416-E4424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703171114. Epub 2017 May 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28507122 Free PMC article.
-
LAMTOR1 depletion induces p53-dependent apoptosis via aberrant lysosomal activation.Cell Death Dis. 2012 Apr 19;3(4):e300. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.39. Cell Death Dis. 2012. PMID: 22513874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta G. P., Massagué J. (2006) Cell 127, 679–695 - PubMed
-
- Nguyen D. X., Massagué J. (2007) Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 341–352 - PubMed
-
- Steeg P. S. (2006) Nat. Med. 12, 895–904 - PubMed
-
- Berger J. C., Vander Griend D. J., Robinson V. L., Hickson J. A., Rinker-Schaeffer C. W. (2005) Cancer Biol. Ther. 4, 805–812 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

