Acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy in adults: imaging findings
- PMID: 21087942
- PMCID: PMC7965708
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2290
Acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy in adults: imaging findings
Abstract
Background and purpose: Acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy has significant morbidity and mortality unless promptly treated. We describe the MR imaging findings of acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy, which are not well-recognized in adult patients.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively reviewed the clinical and imaging data and outcome of consecutive patients with documented hyperammonemic encephalopathy seen at our institution. All patients underwent cranial MR imaging at 1.5T.
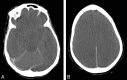
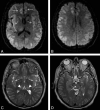
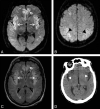
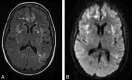
Results: Four patients (2 women; mean age, 42 ± 13 years; range, 24-55 years) were included. Causes included acute fulminant hepatic failure, and sepsis with a background of chronic hepatic failure and post-heart-lung transplantation with various systemic complications. Plasma ammonia levels ranged from 55 to 168 μmol/L. Bilateral symmetric signal-intensity abnormalities, often with associated restricted diffusion involving the insular cortex and cingulate gyrus, were seen in all cases, with additional cortical involvement commonly seen elsewhere but much more variable and asymmetric. Involvement of the subcortical white matter was seen in 1 patient only. Another patient showed involvement of the basal ganglia, thalami, and midbrain. Two patients died (1 with fulminant cerebral edema), and 2 patients survived (1 neurologically intact and the other with significant intellectual impairment).
Conclusions: The striking common imaging finding was symmetric involvement of the cingulate gyrus and insular cortex in all patients, with more variable and asymmetric additional cortical involvement. These specific imaging features should alert the radiologist to the possibility of acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Acute hepatic (or hyperammonemic) encephalopathy: diffuse cortical injury and the significance of ammonia.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011 Aug;32(7):E142; author reply E143. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2622. Epub 2011 Jun 30. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. PMID: 21724572 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Clay AS, Hainline BE. Hyperammonemia in the ICU. Chest 2007;132:1368–78 - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein GR, Yang YX, Nunes FA, et al. . Fatal hyperammonemia after orthotopic lung transplantation. Ann Intern Med 2000;132:283–87 - PubMed
-
- Blaser S, Feigenbaum A. A neuroimaging approach to inborn errors of metabolism. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2004;14:307–29, ix - PubMed
-
- Bindu PS, Sinha S, Taly AB, et al. . Cranial MRI in acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol 2009;41:139–42 - PubMed
-
- Sato S, Yokota C, Toyoda K, et al. . Hyperammonemic encephalopathy caused by urinary tract infection with urinary retention. Eur J Intern Med 2008;19:e78–79 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
