Population exposure to ionising radiation from CT examinations in Aosta Valley between 2001 and 2008
- PMID: 21088089
- PMCID: PMC3473611
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/66718758
Population exposure to ionising radiation from CT examinations in Aosta Valley between 2001 and 2008
Abstract
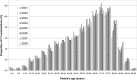
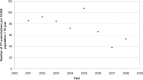
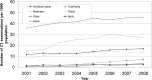
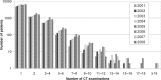
Recent and continuous advances in CT, such as the development of multislice CT, have promoted a rapid increase in its clinical application. Today, CT accounts for approximately 10% of the total number of medical radiographic procedures worldwide. However, the growing performance of the new CT generations have increased not only the diagnostic opportunities, but also the radiation dose to the patient. The relative contribution to the collective radiation dose is now estimated to be approximately 50%. Several papers have been published concerning the intensive use of CT and its contribution to the collective dose. However, most of the literature concerns the years 1997-2003 and the dosimetric evaluations are generally limited to the main standard protocols (chest, head and abdomen), deriving the effective dose by the simple application of the diagnostic reference levels. Only specific dosimetric analyses of single and innovative procedures have been published recently. Moreover, few data comes from Italian radiology departments. This paper aims to bridge these gaps. Firstly, it characterises in terms of measured CT dose index (CTDI) two last-generation scanners of the Radiological Department of Aosta Hospital. Secondly, it evaluates the effective dose from most of the CT examinations performed from 2001 to 2008 to compare protocols and technologies in line with the suggestions of the 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection, Publication 103. Finally, it estimates the collective dose to the population.
Figures
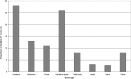
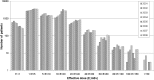
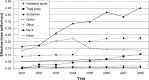
References
-
- Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography – an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med 2007;357:2277–84 - PubMed
-
- Hansen J, Jurik AG. Analysis of current practice of CT examinations. Acta Oncol 2009;48:295–301 - PubMed
-
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) 2000 Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. New York, NY: United Nations, 2000
-
- Shannoun F, Zeeb H, Back C, Blettner M. Medical exposure of the population from diagnostic use of ionizing radiation in Luxembourg between 1994 and 2002. Health Phys 2006;91:154–62 - PubMed
-
- Scanff P, Donadieu J, Pirard P, Aubert B. Population exposure to ionizing radiation from medical examinations in France. Br J Radiol 2008;81:204–13 - PubMed

