Diet-induced impaired glucose tolerance and gestational diabetes in the dog
- PMID: 21088210
- PMCID: PMC3043793
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00768.2010
Diet-induced impaired glucose tolerance and gestational diabetes in the dog
Abstract
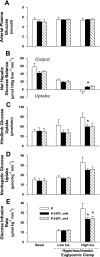
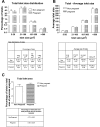
Glucose metabolism was compared in dogs consuming a chow/meat diet throughout pregnancy (P group, n = 6) and dogs switched to a high-fat/high-fructose (HFF) diet during the 4th-5th gestational week (gestation ≃9 wk; P-HFF group; n = 6). An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT; 0.9 g/kg) was administered in the 6th-7th gestational week, and a hyperinsulinemic [0-120 min: 1.8 pmol·kg(-1)·min(-1) (low insulin); 120-240 min: 9 pmol·kg(-1)·min(-1) (high insulin)] euglycemic clamp was performed the following week. Nonpregnant (NP) female dogs underwent OGTTs but not clamp studies. All P-HFF dogs exhibited impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or gestational diabetes (GDM), but only one P dog had IGT. Insulin concentrations in P and P-HFF dogs were significantly lower than in NP dogs 30 and 60 min after the OGTT. Therefore, mean islet size and area were evaluated in P and NP dogs. These values did not differ between groups, and proliferating endocrine cells were rare in pregnancy. During exposure to high insulin, glucose infusion rate and hindlimb glucose uptake were ∼30% greater (P < 0.05) and net hepatic glucose output was more suppressed (-5.5 ± 6.1 vs. 7.8 ± 2.8 mg·100 g liver(-1)·min(-1), P < 0.05) in P than in P-HFF dogs. In conclusion, in the 2nd trimester the canine pancreas does not exhibit islet hypertrophy, hyperplasia, or neogenesis. Combined with the lack of pancreatic adaptation, a HFF diet during late pregnancy produces a canine model of IGT and GDM without hyperinsulinemia but exhibiting liver and muscle insulin resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatic glucose metabolism in late pregnancy: normal versus high-fat and -fructose diet.Diabetes. 2013 Mar;62(3):753-61. doi: 10.2337/db12-0875. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23223020 Free PMC article.
-
A specific metabolomic and lipidomic signature reveals the postpartum resolution of gestational diabetes mellitus or its evolution to type 2 diabetes in rat.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Apr 1;328(4):E493-E512. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00396.2024. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 39947887
-
Gestational diabetes: antepartum characteristics that predict postpartum glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes in Latino women.Diabetes. 1998 Aug;47(8):1302-10. doi: 10.2337/diab.47.8.1302. Diabetes. 1998. PMID: 9703332
-
Gestational diabetes mellitus and subsequent development of overt diabetes mellitus.Dan Med Bull. 1998 Nov;45(5):495-509. Dan Med Bull. 1998. PMID: 9850811 Review.
-
Carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in pregnancy: normal compared with gestational diabetes mellitus.Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 May;71(5 Suppl):1256S-61S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/71.5.1256s. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000. PMID: 10799399 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements and challenges in generating accurate animal models of gestational diabetes mellitus.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Dec 1;305(11):E1327-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00425.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24085033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guidelines for in vivo models of developmental programming of cardiovascular disease risk.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):H221-H241. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00060.2024. Epub 2024 May 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38819382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large animal models in the study of gynecological diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jan 23;11:1110551. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1110551. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36755972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feeding of fish oil and medium-chain triglycerides to canines impacts circulating structural and energetic lipids, endocannabinoids, and non-lipid metabolite profiles.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Aug 24;10:1168703. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1168703. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37691632 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling gestational diabetes mellitus: large animals hold great promise.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Jun;22(2):407-420. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09617-x. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 33245468 Review.
References
-
- Aberg A, Rydhstroem H, Frid A. Impaired glucose tolerance associated with adverse pregnancy outcome: a population-based study in southern Sweden. Am J Obstet Gynecol 184: 77–83, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Andrikopoulos S, Massa CM, Aston-Mourney K, Funkat A, Fam BC, Hull RL, Kahn SE, Proietto J. Differential effect of inbred mouse strain (C57BL/6, DBA/2, 129T2) on insulin secretory function in response to a high fat diet. J Endocrinol 187: 45–53, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Bellamy L, Casas JP, Hingorani AD, Williams D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 373: 1773–1779, 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

