Links between progressive HIV-1 infection of humanized mice and viral neuropathogenesis
- PMID: 21088215
- PMCID: PMC2993281
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100536
Links between progressive HIV-1 infection of humanized mice and viral neuropathogenesis
Abstract
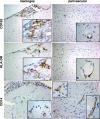
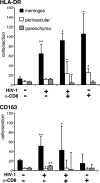
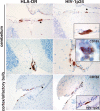
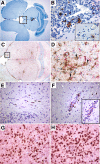
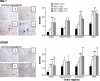
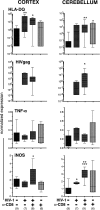
Few rodent models of human immunodeficiency virus type one (HIV-1) infection can reflect the course of viral infection in humans. To this end, we investigated the relationships between progressive HIV-1 infection, immune compromise, and neuroinflammatory responses in NOD/scid-IL-2Rγ(c)(null) mice reconstituted with human hematopoietic CD34(+) stem cells. Human blood-borne macrophages repopulated the meninges and perivascular spaces of chimeric animals. Viral infection in lymphoid tissue led to the accelerated entry of human cells into the brain, marked neuroinflammation, and HIV-1 replication in human mononuclear phagocytes. A meningitis and less commonly an encephalitis followed cM-T807 antibody-mediated CD8(+) cell depletion. We conclude that HIV-1-infected NOD/scid-IL-2Rγ(c)(null) humanized mice can, at least in part, recapitulate lentiviral neuropathobiology. This model of neuroAIDS reflects the virological, immunological, and early disease-associated neuropathological components of human disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generation of cytotoxic T cells against virus-infected human brain macrophages in a murine model of HIV-1 encephalitis.J Immunol. 2002 Apr 15;168(8):3941-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.8.3941. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11937550
-
Dynamics of memory and naïve CD8+ T lymphocytes in humanized NOD/SCID/IL-2Rgammanull mice infected with CCR5-tropic HIV-1.Vaccine. 2010 May 26;28 Suppl 2:B32-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.154. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20510741
-
Hematopoietic stem cell-engrafted NOD/SCID/IL2Rgamma null mice develop human lymphoid systems and induce long-lasting HIV-1 infection with specific humoral immune responses.Blood. 2007 Jan 1;109(1):212-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-017681. Epub 2006 Sep 5. Blood. 2007. PMID: 16954502
-
The HIV-1 associated dementia complex: a metabolic encephalopathy fueled by viral replication in mononuclear phagocytes.Curr Opin Neurol. 1997 Aug;10(4):319-25. Curr Opin Neurol. 1997. PMID: 9266156 Review.
-
Rodent model systems for studies of HIV-1 associated dementia.Neurotox Res. 2005 Oct;8(1-2):91-106. doi: 10.1007/BF03033822. Neurotox Res. 2005. PMID: 16260388 Review.
Cited by
-
New generation humanized mice for virus research: comparative aspects and future prospects.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):14-28. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.10.007. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Of mice and monkeys: can animal models be utilized to study neurological consequences of pediatric HIV-1 infection?ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Aug 19;6(8):1276-89. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00044. Epub 2015 Jun 19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26034832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteopontin/secreted phosphoprotein-1 behaves as a molecular brake regulating the neuroinflammatory response to chronic viral infection.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Sep 17;17(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01949-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32943056 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models for HIV/AIDS research.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Dec;10(12):852-67. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2911. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23154262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rodent models for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.Trends Neurosci. 2012 Mar;35(3):197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.12.006. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Trends Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22305769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Persidsky Y, Buttini M, Limoges J, Bock P, Gendelman HE. An analysis of HIV-1-associated inflammatory products in brain tissue of humans and SCID mice with HIV-1 encephalitis. J Neurovirol. 1997;3:401–416. - PubMed
-
- Poluektova LY, Munn DH, Persidsky Y, Gendelman HE. Generation of cytotoxic T cells against virus-infected human brain macrophages in a murine model of HIV-1 encephalitis. J Immunol. 2002;168:3941–3949. - PubMed
-
- Poluektova L, Gorantla S, Faraci J, Birusingh K, Dou H, Gendelman HE. Neuroregulatory events follow adaptive immune-mediated elimination of HIV-1-infected macrophages: studies in a murine model of viral encephalitis. J Immunol. 2004;172:7610–7617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS036126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1 R01MH083516/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01MH64570/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS031492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS31492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI042845/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA026146/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01 NS034239/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 MH064570/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083516/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS060642/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034239/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI42845/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01DA028555-01/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS043985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA028555/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS060642-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1 P01 NS043985-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01 NS36126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20DA026146/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

