Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation
- PMID: 21088257
- PMCID: PMC3017236
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1934
Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation
Abstract
Purpose: To study the role of drug transporters in central nervous system (CNS) penetration and cellular accumulation of erlotinib and its metabolite, OSI-420.
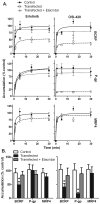
Experimental design: After oral erlotinib administration to wild-type and ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter-knockout mice (Mdr1a/b(-/-), Abcg2(-/-), Mdr1a/b(-/-)Abcg2(-/-), and Abcc4(-/-)), plasma was collected and brain extracellular fluid (ECF) was sampled using intracerebral microdialysis. A pharmacokinetic model was fit to erlotinib and OSI-420 concentration-time data, and brain penetration (P(Brain)) was estimated by the ratio of ECF-to-unbound plasma area under concentration-time curves. Intracellular accumulation of erlotinib was assessed in cells overexpressing human ABC transporters or SLC22A solute carriers.
Results: P(Brain) in wild-type mice was 0.27 ± 0.11 and 0.07 ± 0.02 (mean ± SD) for erlotinib and OSI-420, respectively. Erlotinib and OSI-420 P(Brain) in Abcg2(-/-) and Mdr1a/b(-/-)Abcg2(-/-) mice were significantly higher than in wild-type mice. Mdr1a/b(-/-) mice showed similar brain ECF penetration as wild-type mice (0.49 ± 0.37 and 0.04 ± 0.02 for erlotinib and OSI-420, respectively). In vitro, erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation was significantly lower in cells overexpressing breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) than in control cells. Only OSI-420, not erlotinib, showed lower accumulation in cells overexpressing P-glycoprotein (P-gp) than in control cells. The P-gp/BCRP inhibitor elacridar increased erlotinib and OSI-420 accumulation in BCRP-overexpressing cells. Erlotinib uptake was higher in OAT3- and OCT2-transfected cells than in empty vector control cells.
Conclusion: Abcg2 is the main efflux transporter preventing erlotinib and OSI-420 penetration in mouse brain. Erlotinib and OSI-420 are substrates for SLC22A family members OAT3 and OCT2. Our findings provide a mechanistic basis for erlotinib CNS penetration, cellular uptake, and efflux mechanisms.
©2010 AACR.
Figures

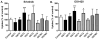

Similar articles
-
Effect of the ATP-binding cassette drug transporters ABCB1, ABCG2, and ABCC2 on erlotinib hydrochloride (Tarceva) disposition in in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies employing Bcrp1-/-/Mdr1a/1b-/- (triple-knockout) and wild-type mice.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Aug;7(8):2280-7. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2250. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18723475
-
Kinetic analysis of the cooperation of P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp/Abcg2) in limiting the brain and testis penetration of erlotinib, flavopiridol, and mitoxantrone.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Jun;333(3):788-96. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.162321. Epub 2010 Mar 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20304939
-
Restricted brain penetration of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib due to the drug transporters P-gp and BCRP.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Apr;30(2):443-9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9569-1. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 20963470
-
Compartment-specific roles of ATP-binding cassette transporters define differential topotecan distribution in brain parenchyma and cerebrospinal fluid.Cancer Res. 2009 Jul 15;69(14):5885-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0700. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19567673 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in mammalian haem transport.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Mar;31(3):182-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.01.005. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16487711 Review.
Cited by
-
[Research Progress of Mechanisms on Intracranial Metastasis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer after Clinical Benefit from EGFR-TKI].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 Aug;18(8):518-22. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.08.09. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26302350 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Leptomeningeal metastasis from systemic cancer: Review and update on management.Cancer. 2018 Jan 1;124(1):21-35. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30911. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29165794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular aspects of drug resistance in cancers.Daru. 2024 Dec 9;33(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s40199-024-00545-8. Daru. 2024. PMID: 39652186 Review.
-
Molecular targeted therapy: A new avenue in glioblastoma treatment.Oncol Lett. 2022 Dec 15;25(2):46. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13632. eCollection 2023 Feb. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36644133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging-guided microdialysis cannula implantation in a spontaneous high-grade glioma murine model.J Pharm Sci. 2011 Oct;100(10):4210-4. doi: 10.1002/jps.22723. Epub 2011 Aug 11. J Pharm Sci. 2011. PMID: 21837651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–32. - PubMed
-
- Ling J, Johnson KA, Miao Z, et al. Metabolism and excretion of erlotinib, a small molecule inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in healthy male volunteers. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006;34:420–6. - PubMed
-
- Moyer JD, Barbacci EG, Iwata KK, et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4838–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

