Microglial P2X₇ receptor expression is accompanied by neuronal damage in the cerebral cortex of the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21088470
- PMCID: PMC3041940
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.1.001
Microglial P2X₇ receptor expression is accompanied by neuronal damage in the cerebral cortex of the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
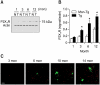
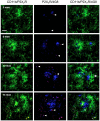
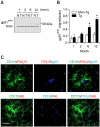
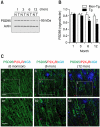
The possibility that P2X₇ receptor (P2X₇R) expression in microglia would mediate neuronal damage via reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was examined in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD). P2X7R was predominantly expressed in CD11b-immunopositive microglia from 3 months of age before Abeta plaque formation. In addition, gp91phox, a catalytic subunit of NADPH oxidase, and ethidium fluorescence were detected in P2X₇R-positive microglial cells of animals at 6 months of age, indicating that P2X₇R-positive microglia could produce ROS. Postsynaptic density 95-positive dendrites showed significant damage in regions positive for P2X₇R in the cerebral cortex of 6 month-old mice. Taken together, up-regulation of P2X₇R activation and ROS production in microglia are parallel with Aβ increase and correlate with synaptotoxicity in AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 (SOCS3) in Altering Activated Microglia Phenotype in APPswe/PS1dE9 Mice.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(3):1235-1247. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160887. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27814300
-
S14G-humanin improves cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid pathology in the middle-aged APPswe/PS1dE9 mice.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Jan;100(3):361-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.09.012. Epub 2011 Oct 2. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012. PMID: 21993310
-
Accelerated microglial pathology is associated with Aβ plaques in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.Aging Cell. 2014 Aug;13(4):584-95. doi: 10.1111/acel.12210. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Aging Cell. 2014. PMID: 24641683 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease.BMC Neurosci. 2008 Dec 3;9 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-9-S2-S8. BMC Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19090996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
Cited by
-
Druggable targets for Parkinson's disease: transcriptomics based Mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;14(1):25763. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77401-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468243 Free PMC article.
-
ATP as a multi-target danger signal in the brain.Front Neurosci. 2015 Apr 28;9:148. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00148. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25972780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal and glial purinergic receptors functions in neuron development and brain disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Oct 28;7:197. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00197. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24191147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic Signaling of ATP in COVID-19 Associated Guillain-Barré Syndrome.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021 Mar;16(1):48-58. doi: 10.1007/s11481-020-09980-1. Epub 2021 Jan 18. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33462776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Features of microglia and neuroinflammation relevant to environmental exposure and neurotoxicity.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2011 Jul;8(7):2980-3018. doi: 10.3390/ijerph8072980. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21845170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O'Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianca VD, Dusi S, Bianchini E, Dal Pra I, Rossi F. Beta-amyloid activates the O-2 forming NADPH oxidase in microglia, monocytes, and neutrophils. A possible inflammatory mechanism of neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15493–15499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
