The role of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 21088684
- PMCID: PMC4662256
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn2935
The role of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Parkinson's disease, like many common age-related conditions, is now recognized to have a substantial genetic component. Here, I discuss how mutations in a large complex gene--leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2)--affect protein function, and I review recent evidence that LRRK2 mutations affect pathways that involve other proteins that have been implicated in Parkinson's disease, specifically α-synuclein and tau. These concepts can be used to understand disease processes and to develop therapeutic opportunities for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
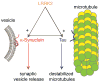
Figures

References
-
- Lees AJ, Hardy J, Revesz T. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2009;373:2055–66. - PubMed
-
- Gasser T. Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009;11:e22. - PubMed
-
- Satake W, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1303–7. - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

