Protein expression profiles distinguish between experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and Pseudomonas pneumonia
- PMID: 21089047
- PMCID: PMC3859317
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200900768
Protein expression profiles distinguish between experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and Pseudomonas pneumonia
Abstract
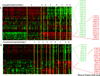
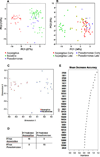
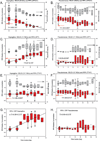
We hypothesized that invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) may generate a distinctive proteomic signature in plasma and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). Proteins in plasma and BAL from two neutropenic rabbit models of IPA and Pseudomonas pneumonia were analyzed by SELDI-TOF MS. Hierarchical clustering analysis of plasma time course spectra demonstrated two clusters of peaks that were differentially regulated between IPA and Pseudomonas pneumonia (57 and 34 peaks, respectively, p<0.001). PCA of plasma proteins demonstrated a time-dependent separation of the two infections. A random forest analysis that ranked the top 30 spectral points distinguished between late Aspergillus and Pseudomonas pneumonias with 100% sensitivity and specificity. Based on spectral data analysis, three proteins were identified using SDS-PAGE and LC/MS and quantified using reverse phase arrays. Differences in the temporal sequence of plasma haptoglobin (p<0.001), apolipoprotein A1 (p<0.001) and transthyretin (p<0.038) were observed between IPA and Pseudomonas pneumonia, as was C-reactive protein (p<0.001). In summary, proteomic analysis of plasma and BAL proteins of experimental Aspergillus and Pseudomonas pneumonias demonstrates unique protein profiles with principal components and spectral regions that are shared in early infection and diverge at later stages of infection. Haptoglobin, apolipoprotein A1, transthyretin, and C-reactive protein are differentially expressed in these infections suggesting important contributions to host defense against IPA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial or commercial conflicts of interest to declare regarding the content of this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Petricoin E, Wulfkuhle J, Espina V, Liotta LA. Clinical proteomics: revolutionizing disease detection and patient tailoring therapy. J Proteome Res. 2004;3:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Liotta LA, Ferrari M, Petricoin E. Clinical proteomics: written in blood. Nature. 2003;425:905. - PubMed
-
- Petricoin EF, Liotta LA. SELDI-TOF-based serum proteomic pattern diagnostics for early detection of cancer. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2004;15:24–30. - PubMed
-
- Liu XP, Shen J, Li ZF, Yan L, Gu J. A serum proteomic pattern for the detection of colorectal adenocarcinoma using surface enhanced laser desorption and ionization mass spectrometry. Cancer Invest. 2006;24:747–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

