Assessment of copy number variation using the Illumina Infinium 1M SNP-array: a comparison of methodological approaches in the Spanish Bladder Cancer/EPICURO study
- PMID: 21089066
- PMCID: PMC3230937
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.21398
Assessment of copy number variation using the Illumina Infinium 1M SNP-array: a comparison of methodological approaches in the Spanish Bladder Cancer/EPICURO study
Abstract
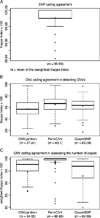
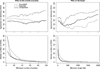
High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-array technologies allow to investigate copy number variants (CNVs) in genome-wide scans and specific calling algorithms have been developed to determine CNV location and copy number. We report the results of a reliability analysis comparing data from 96 pairs of samples processed with CNVpartition, PennCNV, and QuantiSNP for Infinium Illumina Human 1Million probe chip data. We also performed a validity assessment with multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) as a reference standard. The number of CNVs per individual varied according to the calling algorithm. Higher numbers of CNVs were detected in saliva than in blood DNA samples regardless of the algorithm used. All algorithms presented low agreement with mean Kappa Index (KI) <66. PennCNV was the most reliable algorithm (KI(w=) 98.96) when assessing the number of copies. The agreement observed in detecting CNV was higher in blood than in saliva samples. When comparing to MLPA, all algorithms identified poorly known copy aberrations (sensitivity = 0.19-0.28). In contrast, specificity was very high (0.97-0.99). Once a CNV was detected, the number of copies was truly assessed (sensitivity >0.62). Our results indicate that the current calling algorithms should be improved for high performance CNV analysis in genome-wide scans. Further refinement is required to assess CNVs as risk factors in complex diseases.
© 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Bae JS, Cheong HS, Kim JO, Lee SO, Kim EM, Lee HW, Kim S, Kim JW, Cui T, Inoue I, Shin HD. Identification of SNP markers for common CNV regions and association analysis of risk of subarachnoid aneurysmal hemorrhage in Japanese population. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373:593–596. - PubMed
-
- Blauw HM, Veldink JH, van Es MA, van Vught PW, Saris CG, van der Zwaag B, Franke L, Burbach JP, Wokke JH, Ophoff RA, van den Berg LH. Copy-number variation in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a genome-wide screen. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:319–326. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Measure. 1960;20:37–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

