Effects of multiple-interaction photon events in a high-resolution PET system that uses 3-D positioning detectors
- PMID: 21089785
- PMCID: PMC2962664
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3483262
Effects of multiple-interaction photon events in a high-resolution PET system that uses 3-D positioning detectors
Abstract
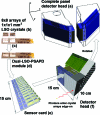
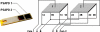
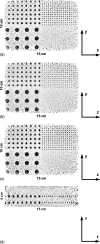
Purpose: The authors' laboratory is developing a dual-panel, breast-dedicated PET system. The detector panels are built from dual-LSO-position-sensitive avalanche photodiode (PSAPD) modules-units holding two 8 x 8 arrays of 1 mm3 LSO crystals, where each array is coupled to a PSAPD. When stacked to form an imaging volume, these modules are capable of recording the 3-D coordinates of individual interactions of a multiple-interaction photon event (MIPE). The small size of the scintillation crystal elements used increases the likelihood of photon scattering between crystal arrays. In this article, the authors investigate how MIPEs impact the system photon sensitivity, the data acquisition scheme, and the quality and quantitative accuracy of reconstructed PET images.
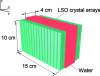
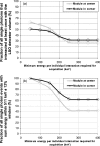
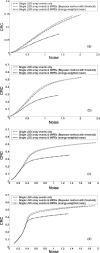
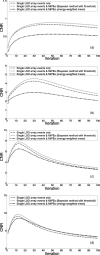
Methods: A Monte Carlo simulated PET scan using the dual-panel system was performed on a uniformly radioactive phantom for the photon sensitivity study. To establish the impact of MIPEs on a proposed PSAPD multiplexing scheme, experimental data were collected from a dual-LSO-PSAPD module edge-irradiated with a 22Na point source, the data were compared against simulation data based on an identical setup. To assess the impact of MIPEs on the dual-panel PET images, a simulated PET of a phantom comprising a matrix of hot spherical radiation sources of varying diameters immersed in a warm background was performed. The list-mode output data were used for image reconstruction, where various methods were used for estimating the location of the first photon interaction in MIPEs for more accurate line of response positioning. The contrast recovery coefficient (CRC), contrast to noise ratio (CNR), and the full width at half maximum spatial resolution of the spheres in the reconstructed images were used as figures of merit to facilitate comparison.
Results: Compared to image reconstruction employing only events with interactions confined to one LSO array, a potential single photon sensitivity gain of > 46.9% (> 115.7% for coincidence) was noted for a uniform phantom when MIPEs with summed-energy falling within a +/- 12% window around the photopeak were also included. Both experimental and simulation data demonstrate that < 0.4% of the events whose summed-energy deposition falling within that energy window interacted with both crystal arrays within the same dual-LSO-PSAPD module. This result establishes the feasibility of a proposed multiplexed readout of analog output signals of the two PSAPDs within each module. Using MIPEs with summed-energy deposition within the 511 keV +/- 12% photopeak window and a new method for estimating the location of the first photon interaction in MIPEs, the corresponding reconstructed image exhibited a peak CNR of 7.23 for the 8 mm diameter phantom spheres versus a CNR of 6.69 from images based solely on single LSO array interaction events. The improved system photon sensitivity could be exploited to reduce the scan time by up to approximately 10%, while still maintaining image quality comparable to that achieved if MIPEs were excluded.
Conclusions: MIPE distribution in the detectors allows the proposed photodetector multiplexing arrangement without significant information loss. Furthermore, acquiring MIPEs can enhance system photon sensitivity and improve PET image CNR and CRC. The system under development can therefore competently acquire and analyze MIPEs and produce high-resolution PET images.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of system geometry and other physical factors on photon sensitivity of high-resolution positron emission tomography.Phys Med Biol. 2007 Jul 7;52(13):3753-72. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/13/007. Epub 2007 May 29. Phys Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17664575 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility study of a point-of-care positron emission tomography system with interactive imaging capability.Med Phys. 2019 Apr;46(4):1798-1813. doi: 10.1002/mp.13397. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30667069 Free PMC article.
-
Design study of a high-resolution breast-dedicated PET system built from cadmium zinc telluride detectors.Phys Med Biol. 2010 May 7;55(9):2761-88. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/9/022. Epub 2010 Apr 19. Phys Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20400807 Free PMC article.
-
Recent development in PET instrumentation.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010 Sep 1;11(6):555-71. doi: 10.2174/138920110792246555. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20497121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative imaging of 124I and 86Y with PET.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011 May;38 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S10-8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1768-2. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21484385 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Physical effects of mechanical design parameters on photon sensitivity and spatial resolution performance of a breast-dedicated PET system.Med Phys. 2010 Nov;37(11):5838-49. doi: 10.1118/1.3484059. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 21158296 Free PMC article.
-
Study of electrode pattern design for a CZT-based PET detector.Phys Med Biol. 2014 Jun 7;59(11):2599-621. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/11/2599. Epub 2014 May 1. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24786208 Free PMC article.
-
Initial performance studies of a wearable brain positron emission tomography camera based on autonomous thin-film digital Geiger avalanche photodiode arrays.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017 Jan;4(1):011003. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.1.011003. Epub 2016 Nov 22. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017. PMID: 27921074 Free PMC article.
-
Study of a high-resolution, 3D positioning cadmium zinc telluride detector for PET.Phys Med Biol. 2011 Mar 21;56(6):1563-84. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/56/6/004. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Phys Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21335649 Free PMC article.
-
Analog signal multiplexing for PSAPD-based PET detectors: simulation and experimental validation.Phys Med Biol. 2010 Dec 7;55(23):7149-74. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/23/001. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Phys Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21081831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang J., Foudray A. M. K., Olcott P. D., Farrell R., Shah K., and Levin C. S., “Performance characterization of a novel thin position-sensitive avalanche photodiode for 1 mm resolution positron emission tomography,” IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. IETNAE 54(3), 415–421 (2007).10.1109/TNS.2007.894128 - DOI
-
- Olcott P. D., Lau F. W. Y., and Levin C. S., “Data acquisition system design for a 1 mm3 resolution PSAPD-based PET system,” Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, 2007 (NSS ‘07), 26 October–3 November 2007. (IEEE, Honolulu, 2007), Vol. 5, pp. 3206–3211.
-
- Vandenbroucke A. and Levin C. S., “Study of scintillation crystal array parameters for an advanced PET scanner dedicated to breast cancer Imaging,” Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record, 2008 (NSS ’08) (IEEE, Dresden, 2008), pp. 4914–4919.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

