Blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 by ipilimumab results in dysregulation of gastrointestinal immunity in patients with advanced melanoma
- PMID: 21090563
- PMCID: PMC2999944
Blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 by ipilimumab results in dysregulation of gastrointestinal immunity in patients with advanced melanoma
Abstract
Blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) by ipilimumab leads to immune-mediated tumor regression and immune-related adverse events (irAEs), including diarrhea and colitis. The current analyses were undertaken to promote an understanding of the underlying mechanism of action and to identify potential biomarkers that could help in the prediction and management of ipilimumab-induced gastrointestinal irAEs. Treatment-naïve or previously treated patients with unresectable stage III/IV melanoma (n = 115) received open-label ipilimumab (10 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four doses) and were randomized to receive concomitant blinded prophylactic oral budesonide (9 mg/d with gradual taper through week 16) or placebo. Outcome measures included histologic assessment of bowel biopsies and assessment of serologic markers of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), fecal calprotectin levels, and polymorphisms in immune-related genes. Ipilimumab resulted in dysregulation of gastrointestinal mucosal immunity as evidenced by altered antibody levels to enteric flora, inflammatory cell infiltration into gastrointestinal mucosa, and increased fecal calprotectin associated with diarrhea and clinical evidence of colitis. The pattern of ipilimumab-induced antibody titers to microbial flora and the histologic features and location of the inflammation were distinct from classic IBD. Prophylactic budesonide did not prevent ipilimumab-induced bowel inflammation. Despite an observed association between colonic inflammation and grade 2 or higher diarrhea, no baseline biomarkers could reliably predict development of gastrointestinal toxicity. Although classic IBD and ipilimumab-related gastrointestinal toxicity are both immune mediated, the observed pattern of biomarkers suggests ipilimumab-related gastrointestinal toxicity may be a distinct clinicopathologic entity.
Figures


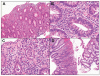
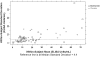


References
-
- Peggs KS, Quezada SA, Korman AJ, Allison JP. Principles and use of anti-CTLA4 antibody in human cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18:206–213. - PubMed
-
- O'Day SJ, Hamid O, Urba WJ. Targeting cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4): a novel strategy for the treatment of melanoma and other malignancies. Cancer. 2007;110:2614–2627. - PubMed
-
- Weber J, Thompson JA, Hamid O, Minor D, Amin A, Ron I, Ridolfi R, Assi H, Maraveyas A, Berman D, Siegel J, O'Day SJ. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II study comparing the tolerability and efficacy of ipilimumab administered with or without prophylactic budesonide in patients with unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:5591–5598. - PubMed
-
- Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W, van den Eertwegh AJ, Lutzky J, Lorigan P, Vaubel JM, Linette GP, Hogg D, Ottensmeier CH, Lebbé C, Peschel C, Quirt I, Clark JI, Wolchok JD, Weber JS, Tian J, Yellin MJ, Nichol GM, Hoos A, Urba WJ. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–723. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
