Efavirenz binding site in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase monomers
- PMID: 21090588
- PMCID: PMC3010390
- DOI: 10.1021/bi101480z
Efavirenz binding site in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase monomers
Abstract
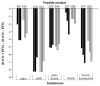
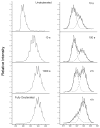
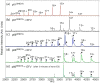
Efavirenz (EFV) is a potent nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) used in the treatment of AIDS. NNRTIs bind in a hydrophobic pocket located in the p66 subunit of reverse transcriptase (RT), which is not present in crystal structures of RT without an inhibitor. Recent studies showed that monomeric forms of the p66 and p51 subunits bind efavirenz with micromolar affinity. The effect of efavirenz on the solution conformations of p66 and p51 monomers was studied by hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HXMS) and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS). HXMS data reveal that five peptides, four of which contain efavirenz contact residues seen in the crystal structure of the RT-EFV complex, exhibit a reduced level of exchange in monomer-EFV complexes. Moreover, peptide 232-246 undergoes slow cooperative unfolding-refolding in the bound monomers, but at a rate much slower than that observed in the p66 subunit of the RT heterodimer [Seckler, J. M., Howard, K. J., Barkley, M. D., and Wintrode, P. L. (2009) Biochemistry 48, 7646-7655]. These results suggest that the efavirenz binding site on p66 and p51 monomers is similar to the NNRTI binding pocket in the p66 subunit of RT. Nanoelectrospray ionization FT-ICR mass spectra indicate that the intact monomers each have (at least) two different conformations. In the presence of efavirenz, the mass spectra change significantly and suggest that p51 adopts a single, more compact conformation, whereas p66 undergoes facile, electrospray-induced cleavage. The population shift is consistent with a selected-fit binding mechanism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Allosteric suppression of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase structural dynamics upon inhibitor binding.Biophys J. 2011 Jan 5;100(1):144-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.11.004. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21190666 Free PMC article.
-
Efavirenz binding to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase monomers and dimers.Biochemistry. 2010 Jan 26;49(3):601-10. doi: 10.1021/bi901579y. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20039714 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of efavirenz binding on the subunit equilibria of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.Biochemistry. 2006 Mar 7;45(9):2779-89. doi: 10.1021/bi051915z. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16503633
-
Conformational changes in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase induced by nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor binding.Curr HIV Res. 2004 Oct;2(4):323-32. doi: 10.2174/1570162043351093. Curr HIV Res. 2004. PMID: 15544453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efavirenz a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor of first-generation: Approaches based on its medicinal chemistry.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Jan 27;108:455-465. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.11.025. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26708112 Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric suppression of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase structural dynamics upon inhibitor binding.Biophys J. 2011 Jan 5;100(1):144-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.11.004. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21190666 Free PMC article.
-
Differential isotopic enrichment to facilitate characterization of asymmetric multimeric proteins using hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2015 Apr 7;87(7):4015-4022. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00372. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25763479 Free PMC article.
-
The HIV-1 p66 homodimeric RT exhibits different conformations in the binding-competent and -incompetent NNRTI site.Proteins. 2017 Dec;85(12):2191-2197. doi: 10.1002/prot.25383. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Proteins. 2017. PMID: 28905420 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated chemical biology approach reveals the mechanism of action of HIV replication inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Dec 1;25(23):6248-6265. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.03.061. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28442262 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical Characterization of p51 and p66 Monomers of HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase with Their Inhibitors.Protein J. 2023 Dec;42(6):741-752. doi: 10.1007/s10930-023-10156-y. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Protein J. 2023. PMID: 37728788
References
-
- Kohlstaedt LA, Wang J, Friedman JM, Rice PA, Steitz TA. Crystal structure at 3.5 Å resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992;256:1783–1790. - PubMed
-
- Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE. Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Woodbury, NY: 1997. - PubMed
-
- Sluis-Cremer N, Arion D, Abram ME, Parniak MA. Proteolytic processing of an HIV-1 pol polyprotein precursor: insights into the mechanism of reverse transcriptase p66/p51 heterodimer formation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1836–1847. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

