Non-stop mRNA decay initiates at the ribosome
- PMID: 21091502
- PMCID: PMC3056498
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07396.x
Non-stop mRNA decay initiates at the ribosome
Abstract
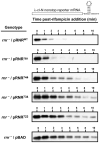
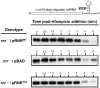
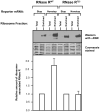
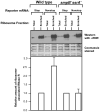
The translation machinery deciphers genetic information encoded within mRNAs to synthesize proteins needed for various cellular functions. Defective mRNAs that lack in-frame stop codons trigger non-productive stalling of ribosomes. We investigated how cells deal with such defective mRNAs, and present evidence to demonstrate that RNase R, a processive 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease, is recruited to stalled ribosomes for the specific task of degrading defective mRNAs. The recruitment process is selective for non-stop mRNAs and is dependent on the activities of SmpB protein and tmRNA. Most intriguingly, our analysis reveals that a unique structural feature of RNase R, the C-terminal lysine-rich (K-rich) domain, is required both for productive ribosome engagement and targeted non-stop mRNA decay activities of the enzyme. These findings provide new insights into how a general RNase is recruited to the translation machinery and highlight a novel role for the ribosome as a platform for initiating non-stop mRNA decay.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Atkins JF, Gesteland RF. A case for trans translation. Nature. 1996;379:769–771. - PubMed
-
- Dulebohn D, Choy J, Sundermeier T, Okan N, Karzai AW. Trans-translation: the tmRNA-mediated surveillance mechanism for ribosome rescue, directed protein degradation, and nonstop mRNA decay. Biochemistry. 2007;46:4681–4693. - PubMed
-
- Frazao C, McVey CE, Amblar M, Barbas A, Vonrhein C, Arraiano CM, Carrondo MA. Unravelling the dynamics of RNA degradation by ribonuclease II and its RNA-bound complex. Nature. 2006;443:110–114. - PubMed
-
- Gillet R, Felden B. Emerging views on tmRNA-mediated protein tagging and ribosome rescue. Molecular microbiology. 2001;42:879–886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

