The novel Aurora A kinase inhibitor MLN8237 is active in resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia and significantly increases the efficacy of nilotinib
- PMID: 21091633
- PMCID: PMC4394217
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01218.x
The novel Aurora A kinase inhibitor MLN8237 is active in resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia and significantly increases the efficacy of nilotinib
Abstract
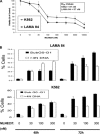
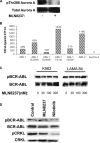
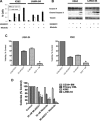
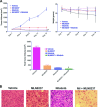
Novel therapies are urgently needed to prevent and treat tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). MLN8237 is a novel Aurora A kinase inhibitor under investigation in multiple phase I and II studies. Here we report that MLN8237 possessed equipotent activity against Ba/F3 cells and primary CML cells expressing unmutated and mutated forms of breakpoint cluster region-Abelson kinase (BCR-ABL). Notably, this agent retained high activity against the T315I and E255K BCR-ABL mutations, which confer the greatest degree of resistance to standard therapy. MLN8237 treatment disrupted cell cycle kinetics, induced apoptosis, caused a dose-dependent reduction in the expression of the large inhibitor of apoptosis protein Apollon, and produced a morphological phenotype consistent with Aurora A kinase inhibition. In contrast to other Aurora kinase inhibitors, MLN8237 did not significantly affect BCR-ABL activity. Moreover, inhibition of Aurora A with MLN8237 significantly increased the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of nilotinib. Targeted knockdown of Apollon sensitized CML cells to nilotinib-induced apoptosis, indicating that this is an important factor underlying MLN8237's ability to increase the efficacy of nilotinib. Our collective data demonstrate that this combination strategy represents a novel therapeutic approach for refractory CML that has the potential to suppress the emergence of T315I mutated CML clones.
© 2011 The Authors Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine © 2011 Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–17. - PubMed
-
- de Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS, et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: incidence of sustained responses in an intention-to-treat analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3358–63. - PubMed
-
- Talpaz M, Silver RT, Druker BJ, et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase 2 study. Blood. 2002;99:1928–37. - PubMed
-
- Volpe G, Panuzzo C, Ulisciani S, et al. Imatinib resistance in CML. Cancer letters. 2009;274:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer cell. 2005;7:129–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

