NAD+ depletion or PAR polymer formation: which plays the role of executioner in ischaemic cell death?
- PMID: 21091637
- PMCID: PMC3135708
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02229.x
NAD+ depletion or PAR polymer formation: which plays the role of executioner in ischaemic cell death?
Abstract
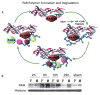
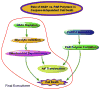
Multiple cell death pathways are activated in cerebral ischaemia. Much of the initial injury, especially in the core of the infarct where cerebral blood flow is severely reduced, is necrotic and secondary to severe energy failure. However, there is considerable evidence that delayed cell death continues for several days, primarily in the penumbral region. As reperfusion therapies grow in number and effectiveness, restoration of blood flow early after injury may lead to a shift towards apoptosis. It is important to elucidate what are the key mediators of apoptotic cell death after stroke, as inhibition of apoptosis may have therapeutic implications. There are two well described pathways that lead to apoptotic cell death; the caspase pathway and the more recently described caspase-independent pathway triggered by poly-ADP-ribose polymers (PARP) activation. Caspase-induced cell death is initiated by release of mitochondrial cytochrome c, formation of the cytosolic apoptosome, and activation of endonucleases leading to a multitude of small randomly cleaved DNA fragments. In contrast caspase-independent cell death is secondary to activation of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF). Mitochondrial AIF translocates to the nucleus, where it induces peripheral chromatin condensation, as well as characteristic high-molecular-weight (50 kbp) DNA fragmentation. Although caspase-independent cell death has been recognized for some time and is known to contribute to ischaemic injury, the upstream triggering events leading to activation of this pathway remain unclear. The two major theories are that ischaemia leads to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) depletion and subsequent energy failure, or alternatively that cell death is directly triggered by a pro-apoptotic factor produced by activation of the DNA repair enzyme PARP. PARP activation is robust in the ischaemic brain producing variable lengths of poly-ADP-ribose (PAR) polymers as byproducts of PARP activation. PAR polymers may be directly toxic by triggering mitochondrial AIF release independently of NAD+ depletion. Recently, sex differences have been discovered that illustrate the importance of understanding these molecular pathways, especially as new therapeutics targeting apoptotic cell death are developed. Cell death in females proceeds primarily via caspase activation whereas caspase-independent mechanisms triggered by the activation of PARP predominate in the male brain. This review summarizes the current literature in an attempt to clarify the roles of NAD+ and PAR polymers in caspase-independent cell death, and discuss sex specific cell death to provide an example of the possible importance of these downstream mediators.
© 2011 The Authors. Acta Physiologica © 2011 Scandinavian Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Abdelkarim GE, Gertz K, Harms C, Katchanov J, Dirnagl U, Szabo C, Endres M. Protective effects of PJ34, a novel, potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in in vitro and in vivo models of stroke. Int J Mol Med. 2001;7:255–60. - PubMed
-
- Alano CC, Ying W, Swanson RA. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated cell death in astrocytes requires NAD+ depletion and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18895–902. - PubMed
-
- Alle H, Roth A, Geiger JR. Energy-efficient action potentials in hippocampal mossy fibers. Science. 2009;325:1405–8. - PubMed
-
- Almeida A, Moncada S, Bolanos JP. Nitric oxide switches on glycolysis through the AMP protein kinase and 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:45–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

