Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 mediates anti-β2GPI/β2GPI-induced tissue factor expression in THP-1 cells
- PMID: 21091668
- PMCID: PMC3043309
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04291.x
Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 mediates anti-β2GPI/β2GPI-induced tissue factor expression in THP-1 cells
Abstract
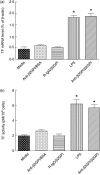
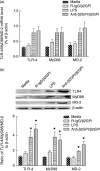
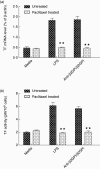
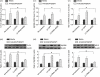
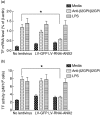
Our previous study demonstrated that annexin A2 (ANX2) on cell surface could function as a mediator and stimulate tissue factor (TF) expression of monocytes by anti-β₂-glycoprotein I/β₂-glycoprotein I complex (anti-β₂GPI/β₂GPI). However, ANX2 is not a transmembrane protein and lacks the intracellular signal transduction pathway. Growing evidence suggests that Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) might act as an 'adaptor' for intracellular signal transduction in anti-β₂GPI/β₂GPI-induced TF expressing cells. In the current study, we investigated the roles of TLR-4 and its related molecules, myeloid differentiation protein 2 (MD-2) and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), in anti-β₂GPI/β₂GPI-induced TF expressing human monocytic-derived THP-1 (human acute monocytic leukaemia) cells. The relationship of TLR-4 and ANX2 in this process was also explored. Along with TF, expression of TLR-4, MD-2 and MyD88 in THP-1 cells increased significantly when treated by anti-β₂GPI (10 µg/ml)/β₂GPI (100 µg/ml) complex. The addition of paclitaxel, which competes with the MD-2 ligand, could inhibit the effects of anti-β₂GPI/β₂GPI on TLR-4, MD-2, MyD88 and TF expression. Both ANX2 and TLR-4 in THP-1 cell lysates could bind to β₂GPI that had been conjugated to a column (β₂GPI-Affi-Gel). Furthermore, TLR-4, MD-2, MyD88 and TF expression was remarkably diminished in THP-1 cells infected with ANX2-specific RNA interference (RNAi) lentivirus (LV-RNAi-ANX2), in spite of treatment with a similar concentration of anti-β₂GPI/β₂GPI complex. These results indicate that TLR-4 and its signal transduction pathway contribute to anti-β₂GPI/β₂GPI-induced TF expression in THP-1 cells, and the effects of TLR-4 with ANX2 are tightly co-operative.
© 2010 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Immunology © 2010 British Society for Immunology.
Figures

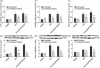

References
-
- de Groot PG, Derksen RH. Antiphospholipid antibodies: update on detection, pathophysiology, and treatment. Curr Opin Hematol. 2004;11:165–9. - PubMed
-
- Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Bas de Laat H, Derksen RH, de Groot PG. beta2-glycoprotein I, the playmaker of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Immunol. 2004;112:161–8. - PubMed
-
- Kinev AV, Roubey RA. Tissue factor in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 2008;17:952–8. - PubMed
-
- Morrissey JH. Tissue factor: an enzyme cofactor and a true receptor. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:66–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

