Dietary fatty acids and the aging brain
- PMID: 21091943
- PMCID: PMC4019000
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00345.x
Dietary fatty acids and the aging brain
Abstract
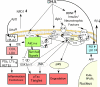
Aging contributes to physiological decline and vulnerability to disease. In the brain, even with minimal neuronal loss, aging increases oxidative damage, inflammation, demyelination, impaired processing, and metabolic deficits, particularly during pathological brain aging. In this review, the possible role of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in the prevention of age-related disruption of brain function is discussed. High-fat diabetogenic diets, cholesterol, and the omega-6 fatty acid arachidonate and its prostaglandin metabolites have all been implicated in promoting the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Evidence presented here shows DHA acts to oppose this, exerting a plethora of pleiotropic activities to protect against the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
© 2010 International Life Sciences Institute.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DHA may prevent age-related dementia.J Nutr. 2010 Apr;140(4):869-74. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.113910. Epub 2010 Feb 24. J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20181786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary omega 3 fatty acids and the developing brain.Brain Res. 2008 Oct 27;1237:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.08.078. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18789910 Review.
-
Dietary docosahexaenoic acid supplementation prevents age-related functional losses and A2E accumulation in the retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Apr 24;53(4):2256-65. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8569. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22427551
-
Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 2 : macronutrients.J Nutr Health Aging. 2006 Sep-Oct;10(5):386-99. J Nutr Health Aging. 2006. PMID: 17066210 Review.
-
Mechanisms of n-3 fatty acid-mediated development and maintenance of learning memory performance.J Nutr Biochem. 2010 May;21(5):364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.11.003. Epub 2010 Mar 16. J Nutr Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20233652 Review.
Cited by
-
Concurrent training associated with moderate walnut consumption improved isokinetic strength, subjective sleep quality, cognitive performance and postural balance in elderly active men: a randomized controlled trial.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Feb 29;36(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02646-x. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 38421528 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary fat composition and dementia risk.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Sep;35 Suppl 2:S59-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.03.038. Epub 2014 May 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24970568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ecological lipidology.Elife. 2022 Sep 7;11:e79288. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79288. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36069772 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation improves neurologic recovery and attenuates white matter injury after experimental traumatic brain injury.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013 Sep;33(9):1474-84. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.108. Epub 2013 Jun 26. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013. PMID: 23801244 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmalogens Improve Lymphatic Clearance of Amyloid Beta from Mouse Brain and Cognitive Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 22;25(23):12552. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312552. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cole GM, Frautschy SA. The role of insulin and neurotrophic factor signaling in brain aging and Alzheimer's Disease. Exp Gerontol. 2007;42:10–21. - PubMed
-
- Lee CK, Weindruch R, Prolla TA. Gene-expression profile of the ageing brain in mice. Nat Genet. 2000;25:294–297. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Tishler TA, Lu PH, Villablanca P, et al. Brain ferritin iron may influence age- and gender-related risks of neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:414–423. - PubMed
-
- Cummings JL, Cole G. Alzheimer disease. JAMA. 2002;287:2335–2338. - PubMed
-
- Rosendorff C, Beeri MS, Silverman JM. Cardiovascular risk factors for Alzheimer's disease. Am J Geriatr Cardiol. 2007;16:143–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

