The importance of corticosterone in mediating restraint-induced weight loss in rats
- PMID: 21092743
- PMCID: PMC3010503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.11.014
The importance of corticosterone in mediating restraint-induced weight loss in rats
Abstract
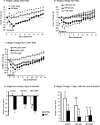
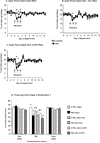
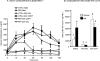
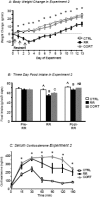
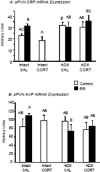
I. J. Scherer, P. V. Holmes, R. B.S. Harris. The importance of corticosterone in mediating restraint-induced weight loss in rats. PHYSIOL BEHAV 00 (0) 000-000, 2010. Rats restrained for 3 h/day for 3d ays (RR) lose weight and do not return to the weight of non-restrained controls once restraint has ended. This study tested the importance of restraint-induced corticosterone release in mediating the change in body weight by injecting ADX rats with 2.0mg corticosterone/kg before each restraint to replicate the restraint-induced surge in circulating corticosterone. Restrained adrenalectomized (ADX) rats injected with corticosterone had the same initial weight loss as intact restrained rats, whereas corticosterone injection in non-restrained ADX rats and restraint of ADX rats injected with saline each produced only half as much initial weight loss. Sustained weight loss, measured for 14 days after the end of RR, was the same for restrained intact rats and restrained ADX rats injected with corticosterone whereas restrained ADX rats injected with saline achieved the same weight gain as their controls. Corticosterone injections had no effect on weight gain of non-restrained intact rats. In situ hybridization showed that corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) mRNA expression in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) was increased by the same degree in ADX rats and restrained intact rats and was not modified by corticosterone injections. There was no significant effect of restraint, ADX or corticosterone injection on PVN arginine vasopressin (AVP) mRNA expression. These data indicate that a surge in corticosterone causes sustained weight loss in ADX rats through a mechanism that can be compensated for in intact rats and is independent of changes in PVN CRF or AVP mRNA expression.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Harris RB, Palmondon J, Leshin S, Flatt WP, Richard D. Chronic disruption of body weight but not of stress peptides or receptors in rats exposed to repeated restraint stress. Horm Behav. 2006;49:615–625. - PubMed
-
- Harris RB, Martin RJ. Recovery of body weight from below “set point” in mature female rats. J Nutr. 1984;114:1143–1150. - PubMed
-
- Harris RB, Kasser TR, Martin RJ. Dynamics of recovery of body composition after overfeeding, food restriction or starvation of mature female rats. J Nutr. 1986;116:2536–2546. - PubMed
-
- Meerlo P, De Boer SF, Koolhaas JM, Daan S, Van den Hoofdakker RH. Changes in daily rhythms of body temperature and activity after a single social defeat in rats. Physiol Behav. 1996;59:735–739. - PubMed
-
- Valles A, Marti O, Garcia A, Armario A. Single exposure to stressors causes long-lasting, stress-dependent reduction of food intake in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;279:R1138–1144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

