The transcription factor Pax6 regulates survival of dopaminergic olfactory bulb neurons via crystallin αA
- PMID: 21092858
- PMCID: PMC4388427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.030
The transcription factor Pax6 regulates survival of dopaminergic olfactory bulb neurons via crystallin αA
Abstract
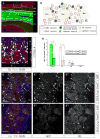
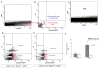
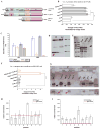
Most neurons in the adult mammalian brain survive for the entire life of an individual. However, it is not known which transcriptional pathways regulate this survival in a healthy brain. Here, we identify a pathway regulating neuronal survival in a highly subtype-specific manner. We show that the transcription factor Pax6 expressed in dopaminergic neurons of the olfactory bulb regulates the survival of these neurons by directly controlling the expression of crystallin αA (CryαA), which blocks apoptosis by inhibition of procaspase-3 activation. Re-expression of CryαA fully rescues survival of Pax6-deficient dopaminergic interneurons in vivo and knockdown of CryαA by shRNA in wild-type mice reduces the number of dopaminergic OB interneurons. Strikingly, Pax6 utilizes different DNA-binding domains for its well-known role in fate specification and this role of regulating the survival of specific neuronal subtypes in the mature, healthy brain.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A dlx2- and pax6-dependent transcriptional code for periglomerular neuron specification in the adult olfactory bulb.J Neurosci. 2008 Jun 18;28(25):6439-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0700-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18562615 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6 is required for making specific subpopulations of granule and periglomerular neurons in the olfactory bulb.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 27;25(30):6997-7003. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1435-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16049175 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a transcription factor Pax6 in the developing vertebrate olfactory system.Dev Growth Differ. 2007 Dec;49(9):683-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2007.00965.x. Epub 2007 Oct 1. Dev Growth Differ. 2007. PMID: 17908181 Review.
-
Pax6 is essential for the maintenance and multi-lineage differentiation of neural stem cells, and for neuronal incorporation into the adult olfactory bulb.Stem Cells Dev. 2014 Dec 1;23(23):2813-30. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0058. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Stem Cells Dev. 2014. PMID: 25117830 Free PMC article.
-
Concise review: Pax6 transcription factor contributes to both embryonic and adult neurogenesis as a multifunctional regulator.Stem Cells. 2008 Jul;26(7):1663-72. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0884. Epub 2008 May 8. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18467663 Review.
Cited by
-
The α crystallin domain of small heat shock protein b8 (Hspb8) acts as survival and differentiation factor in adult hippocampal neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2013 Mar 27;33(13):5785-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6452-11.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23536091 Free PMC article.
-
Crybb2 coding for βB2-crystallin affects sensorimotor gating and hippocampal function.Mamm Genome. 2013 Oct;24(9-10):333-48. doi: 10.1007/s00335-013-9478-7. Epub 2013 Oct 6. Mamm Genome. 2013. PMID: 24096375 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Born Olfactory Bulb Dopaminergic Interneurons: Molecular Determinants and Experience-Dependent Plasticity.Front Neurosci. 2016 May 6;10:189. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00189. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27199651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A dual role for the transcription factor Sp8 in postnatal neurogenesis.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 28;8(1):14560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32134-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30266956 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Shock Proteins Regulatory Role in Neurodevelopment.Front Neurosci. 2018 Nov 12;12:821. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00821. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30483047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alavian KN, Scholz C, Simon HH. Transcriptional regulation of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons: the full circle of life and death. Mov Disord. 2008;23:319–328. - PubMed
-
- Andley UP. Crystallins in the eye: Function and pathology. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2007;26:78–98. - PubMed
-
- Bai F, Xi JH, Andley UP. Up-regulation of tau, a brain microtubule-associated protein, in lens cortical fractions of aged alphaA-, alphaB-, and alphaA/B-crystallin knockout mice. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1589–1600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

