Radiation enhances regulatory T cell representation
- PMID: 21093169
- PMCID: PMC3117954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.09.034
Radiation enhances regulatory T cell representation
Abstract
Purpose: Immunotherapy could be a useful adjunct to standard cytotoxic therapies such as radiation in patients with micrometastatic disease, although successful integration of immunotherapy into treatment protocols will require further understanding of how standard therapies affect the generation of antitumor immune responses. This study was undertaken to evaluate the impact of radiation therapy (RT) on immunosuppressive T regulatory (Treg) cells.
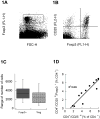
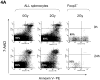
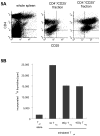
Methods and materials: Treg cells were identified as a CD4(+)CD25(hi)Foxp3(+) lymphocyte subset, and their fate was followed in a murine TRAMP C1 model of prostate cancer in mice with and without RT.
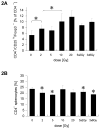
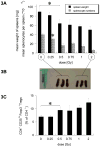
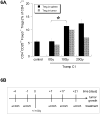
Results: CD4(+)CD25(hi)Foxp3(+) Treg cells increased in immune organs after local leg or whole-body radiation. A large part, but not all, of this increase after leg-only irradiation could be ascribed to radiation scatter and Treg cells being intrinsically more radiation resistant than other lymphocyte subpopulations, resulting in their selection. Their functional activity on a per-cell basis was not affected by radiation exposure. Similar findings were made with mice receiving local RT to murine prostate tumors growing in the leg. The importance of the Treg cell population in the response to RT was shown by systemic elimination of Treg cells, which greatly enhanced radiation-induced tumor regression.
Conclusions: We conclude that Treg cells are more resistant to radiation than other lymphocytes, resulting in their preferential increase. Treg cells may form an important homeostatic mechanism for tissues injured by radiation, and in a tumor context, they may assist in immune evasion during therapy. Targeting this population may allow enhancement of radiotherapeutic benefit through immune modulation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
2-Gy whole-body irradiation significantly alters the balance of CD4+ CD25- T effector cells and CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ T regulatory cells in mice.Cell Mol Immunol. 2010 Nov;7(6):419-27. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.45. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20871628 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral T-cell tolerance associated with prostate cancer is independent from CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells.Cancer Res. 2008 Jan 1;68(1):292-300. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2429. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18172322
-
CD4+CD69+ T cells and CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Treg cells imbalance in peripheral blood, spleen and peritoneal lavage from pristane-induced systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) mice.Adv Rheumatol. 2019 Jul 24;59(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s42358-019-0072-x. Adv Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31340848
-
Gamma-ray resistance of regulatory CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells in mice.Radiat Res. 2010 Feb;173(2):148-57. doi: 10.1667/RR0978.1. Radiat Res. 2010. PMID: 20095846
-
Targeting CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T-cells for the augmentation of cancer immunotherapy.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2007 Dec;8(12):1002-8. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2007. PMID: 18058571 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Neuroinflammation in Brain Cancer: Uncovering Mechanisms, Pharmacological Targets, and Neuropharmaceutical Developments.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 18;12:680021. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.680021. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34084145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caloric Restriction Impairs Regulatory T cells Within the Tumor Microenvironment After Radiation and Primes Effector T cells.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Aug 1;110(5):1341-1349. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.02.029. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33647370 Free PMC article.
-
A hypofractionated radiation regimen avoids the lymphopenia associated with neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy of borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2016 Aug 16;4:45. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0149-6. eCollection 2016. J Immunother Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27532020 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 in Radiotherapy: A Two Headed Signal Regulating Tumor Radiosensitivity and Immunity.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 14;13:6859-6871. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S253772. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment as a Regulator of Radiation Therapy: New Insights into Stromal-Mediated Radioresistance.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 11;12(10):2916. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102916. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liao YP, Wang CC, Butterfield LH, et al. Ionizing radiation affects human MART-1 melanoma antigen processing and presentation by dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2004;173:2462–2469. - PubMed
-
- Tsai CH, Hong JH, Hsieh KF, et al. Tetracycline-regulated intratumoral expression of interleukin-3 enhances the efficacy of radiation therapy for murine prostate cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006;13:1082–1092. - PubMed
-
- Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, et al. Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 2002;169:2756–2761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

