Regulated expression of nuclear receptor RORγt confers distinct functional fates to NK cell receptor-expressing RORγt(+) innate lymphocytes
- PMID: 21093318
- PMCID: PMC3042726
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.017
Regulated expression of nuclear receptor RORγt confers distinct functional fates to NK cell receptor-expressing RORγt(+) innate lymphocytes
Abstract
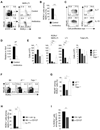
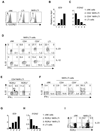
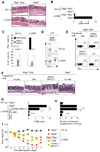
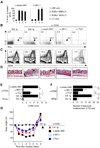
Whether the recently identified innate lymphocyte population coexpressing natural killer cell receptors (NKRs) and the nuclear receptor RORγt is part of the NK or lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cell lineage remains unclear. By using adoptive transfer of genetically tagged LTi-like cells, we demonstrate that NKR⁻RORγt(+) innate lymphocytes but not NK cells were direct progenitors to NKR(+)RORγt(+) cells in vivo. Genetic lineage tracing revealed that the differentiation of LTi-like cells was characterized by the stable upregulation of NKRs and a progressive loss of RORγt expression. Whereas interleukin-7 (IL-7) and intestinal microbiota stabilized RORγt expression within such NKR-LTi cells, IL-12 and IL-15 accelerated RORγt loss. RORγt(+) NKR-LTi cells produced IL-22, whereas RORγt⁻ NKR-LTi cells released IFN-γ and were potent inducers of colitis. Thus, the RORγt gradient in NKR-LTi cells serves as a tunable rheostat for their functional program. Our data also define a previously unappreciated role of RORγt⁻ NKR-LTi cells for the onset or maintenance of inflammatory bowel diseases.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
The LTi cell, an immunologic chameleon.Immunity. 2010 Nov 24;33(5):650-2. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.11.016. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 21094460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aloisi F, Pujol-Borrell R. Lymphoid neogenesis in chronic inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:205–217. - PubMed
-
- Bouskra D, Brezillon C, Berard M, Werts C, Varona R, Boneca IG, Eberl G. Lymphoid tissue genesis induced by commensals through NOD1 regulates intestinal homeostasis. Nature. 2008;456:507–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

