Hdac1 and Hdac2 act redundantly to control p63 and p53 functions in epidermal progenitor cells
- PMID: 21093383
- PMCID: PMC3003338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.015
Hdac1 and Hdac2 act redundantly to control p63 and p53 functions in epidermal progenitor cells
Abstract
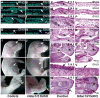
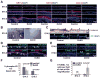
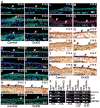
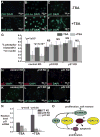
Epidermal and hair follicle development from surface ectodermal progenitor cells requires coordinated changes in gene expression. Histone deacetylases alter gene expression programs through modification of chromatin and transcription factors. We find that deletion of ectodermal Hdac1 and Hdac2 results in dramatic failure of hair follicle specification and epidermal proliferation and stratification, phenocopying loss of the key ectodermal transcription factor p63. Although expression of p63 and its positively regulated basal cell targets is maintained in Hdac1/2-deficient ectoderm, targets of p63-mediated repression, including p21, 14-3-3σ, and p16/INK4a, are ectopically expressed, and HDACs bind and are active at their promoter regions in normal undifferentiated keratinocytes. Mutant embryos display increased levels of acetylated p53, which opposes p63 functions, and p53 is required for HDAC inhibitor-mediated p21 expression in keratinocytes. Our data identify critical requirements for HDAC1/2 in epidermal development and indicate that HDAC1/2 directly mediate repressive functions of p63 and suppress p53 activity.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Akala OO, Park IK, Qian D, Pihalja M, Becker MW, Clarke MF. Long-term haematopoietic reconstitution by Trp53−/−p16Ink4a−/−p19Arf−/− multipotent progenitors. Nature. 2008;453:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Ahn K, Kairo A, Chu EY, Wine-Lee L, Reddy ST, Croft NJ, Cebra-Thomas JA, Metzger D, Chambon P, et al. Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development. 2004;131:2257–2268. - PubMed
-
- Blanpain C, Fuchs E. p63: revving up epithelial stem-cell potential. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:731–733. - PubMed
-
- Brunmeir R, Lagger S, Seiser C. Histone deacetylase HDAC1/HDAC2-controlled embryonic development and cell differentiation. Int J Dev Biol. 2009;53:275–289. - PubMed
-
- Byrne C, Tainsky M, Fuchs E. Programming gene expression in developing epidermis. Development. 1994;120:2369–2383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR055241/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UO1HL100405/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32AR007465/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100405/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007516/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC1DE020337/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- T32HD007516/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR047709/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD053829/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE015342/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071546/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR47709/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD053829/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007465/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071546/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DE020337/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01AR055241/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

